Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are carbohydrates needed for? What are three types of carbohydrates? Where do we get carbs from?
|
Carbohydrates are good sources of energy Sugar, Starch, Fibre We get carbs from foods like pasta, bread, rice, potatoes starchy foods
|
|
Give examples of simple sugars and the scientific name for them Give examples of double sugars and the scientific name for them Why are sugars better than starch?
|
Simple Sugars are also known as monosaccharides, examples of some include glucose and fructose. Simple sugars are absorbed into the body quickly a fast source of energy Double Sugars are also known as disaccharides and examples of them include lactose and sucrose. Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharides. Sugars are better than starches because they are easier to digest
|
|
What is the scientific name for complex sugars? How is it broken down? Why is it good to eat starch before playing sport? What happens to the energy that isnt used?
|
The scientific name for complex sugars are polysaccharides. Starch is a complex sugar Starch is broken down by digestion before the energy is used, from starch into glucose Its good to eat starch before playing sport because it releases energy slowly and the body will be full of glycogen The energy that isnt used is stored in the body as fat so its often carbohydrates and not fats that cause people to be overweight
|
|
What is fibre? What foods contain fibre? Why is fibre important?
|
Fibre is a type of carbohydrate. Fibre is aka NSP (non starch polysaccharide) and is made up of long chains of monosaccharides Foods like Bran, fruit beans and wholemeal contain a lot of fibre Fibre is important because it helps to aid digestion, problems with digestion could lead to constipation or in more severe cases bowel cancer and diverticular disease
|
|
Name types of sugars What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic sugars? What does sugar do? eg jam, biscuits, bread Why are sugar substitutes used? Why are they better for your health? Why are they better for diabetics? Why shouldnt sugar substitutes be used in home baking? Why might people use sugar substitutes
|
Granulated Sugar (kitchen use), Caster Sugar (used for naking), Brown Sugar (strong distinctive flavours), Icing Sugar (for icing and sweets) Sugars originally come from sugar cane, but they can occur naturally in things like fruit and honey also. Intrinsic sugars are those found naturally in cells of fruit and veg, and extrinsic are found in sugar cane, syrup and honey -Sugar makes things sweet, or can soften sharp flavours-Acts as a preservative in jam-In creamed mixtures sugar is beaten with fat which aerates the micture (add air) helps lighten it-Speeds up fermentation e.g, in bread-Adds Colour-Used in caramelisation Sugar substitutes are used because they are sometimes healthier, better for your teeth and contain a lot fewer calories this is why theyre better for diabetics who have to control their sugar intake and good for those on a slimming diet Sugar substitutes shouldnt be used in home baking because they dont have the same aerating properties as cane sugar
|
|
How can starch be used as a bulking agent? How can starch be used as a gelling agent? How can starch be used as a thickening agent?
|
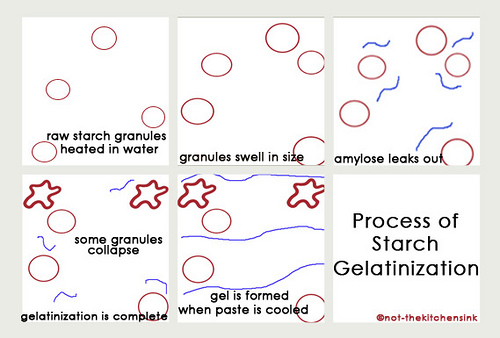 Starch granules swell when a liquid is added and so can provide the bulk of a product. eg the starch in flour makes up most of the volume of the pasta When moisture is added to a starch granule and heat is applied the starch granules begins to absorb the liquid and swell. At 80 degrees the starch granules will burst cauign the liquid to turn thick and viscous. Gelatinisation is complete at 100 degrees. The thickened liquid is now a gel. When starch and a liquid are mixed together the starch particles form a suspension (they dont dissolve). The mixture is stirred to keep the particles suspended, heat is applied which causes thickening |
|
What are modified starches? How can they be used in food preperation? What are the benefits of modified starches?
|
These are starches that have been treated so they react in a certain way in particular conditions. Modified starches are used to thicken things like instant desserts, whipped cream, yoghurts or packet soup. -Normal starches can be affected by acid, so they dont work properly. But some modified starches are immune to this so it can be used to thicken acidic products like salad cream that contains vinegar-When a protein is heated it coagulates, and is squeezes out fat and water, this is called syneresis. Some starch products allow food to be reheated without the occurence of syneresis which is useful for frozen foods, eg lasagnes so that they keep their moisture and nutrients when theyre cooked
|
|
What is gluten? What does gluten give bread? How does gluten help in bread making?
|
Gluten is a protein found in bread. When dough made with flour is kneaded the protein gluten is formed. Gluten gives dough elasticity (stechiness) which helps the bread to rise. When making bread a strong bread flour should be used because it will form more gluten than other types of flour The dough mixture used to make bread contains yeast, which ferments to the sugar to produce carbon dioxide, the gluten stretches to hold the carbon dioxide - this is what makes bread rise. When gluten reaches a high temperature it coagulates.
|
|
What is protein needed for? Why do we need protein? What are the three types of meat eaten in the UK? How do you tenderize meat? How do you stop meat from drying out?
|
Protein is needed for growth and repair , it helps our bodies to build and repair muscles, tissues and organs and helps children to grow. We need protein because our body cant make all the amino acids it needs so we have to eat the amino acides the body cant make (essential amino acids) Beef and Lamb (B vitamins, iron and zinc) Pork (thiamin B1 and niacin B3) You tenderize meat by partly breaking down the fibres in the meat. This can be done by bashing it with a mallet, marinating it in something acidic or cooking it really slowly To stop meat from drying out you can seal the outside of the meat, usually by frying at high temperatures fot a couple of minutes. This helps to retain the juices and flavour of the meat, makes meat more tender and juicy after cooking
|
|
What are three types of poultry? What is poultry a good source of?
|
Chicken, Turkey and Duck they are called white meats however duck is often called a red meat. A good source of protein, B vitamins and are fairly low in saturated fat (especially without the skin)
|
|
What are the three main types of fish and give examples of each? What do fish provide you with?
|
Oily fish e.g herring, mackerel, salmon, tunaWhite fish e.g cod, haddock, plaice, skateShellfish e.g crab, lobster, mussels Fish contains a lot of vitamins plus omega 3 oils, good for a healthy brain help lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and arthritis.
|
|
Why are meat replacements needed? What is tofu made from, what can it be used in? What is TVP and what can it be used in? What is Quorn and what can it be used in? Whats the problem with these meat replacements?
|
Meat replacements are need for the growing number of vegetarians. Vegetarians dont eat meat so they need to get their protein and other nutrients from elsewhere. Beans lentils and nuts are all good sources of proteins. Tofu is a meat replacement, its made from soya and can be made into sausages, burgers and ready meals TVP is textured vegetable protein its also made from soya beans and can be sitr fried and used in desserts Quorn is a mycoprotein, thats made from a mushroom like fungus and egg whites. It can be made into mince for chilli con carne, fillets to serve in sauces and is most commonly used to replace chicken. The meat replacements lack flavour and dont taste of much so they need to be flavoured by marinating them (soaking them in a mixture of things like oil, wine, vinegar and herbs before cooking)
|
|
What are eggs a good source of? What bacteria is associated with eggs? What do manafacturers sometimes used to stop the risk of salmonella? What are the benefits of boiling and poaching eggs? What are the benefits of scrambled eggs? What are the negatives with fried eggs? What is coagulation? Which part of the egg does lecithin come from? What is it?
|
Eggs are a good source of protein, fat (mainly saturated) vitamins A, B2 and D and minerals including iodine. Raw eggs may contain the bacteria salmonella - which causes severe food poisoning. Its very important that eggs are cooked through thoroughly so that all bacteria are destroyed. You should be extra careful when cooking eggs to be eaten by pregnant women, babies and elderly or frail people. To stop the risk of salmonella manafacturers often used dried or pasteaurised egg Boiled and poached eggs are nice and healthy because theyre cooked using no fat Scrambled eggs are healthy also if not using fat Fried eggs can absorb a lot of fat, its best to use oils with unsaturated fat and drain off as much oil as possible before eating Coagulation is when the egg whit becomes more solid the temperatures for this are 60 degrees and 70 degrees it stays solid and thickened Lecithin if found in egg yolks it keeps an emulsion stable stops them from seperating again
|
|
Why do we need fats? What are the 6 main types of fats and oils? What is shortening? What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fat? List 2 functions of fat in pastry making What is cholesterol? Why are high cholesterol levels bad?
|
We need fats for body warmth and insulation. Fats are a concentrated source of energy, theyre a source of Vitamins A, D,E & K, they provide us with fatty acids which are essential for our body cells. -Butter made from churning cream-Margerine made from vegetable oils blended with other stuff-Lard made from pig fat-Suet is made from fat which protects animals vital organs-Oils come from pressed seeds (e.g rapeseed, sunflower seed)-Low fat spreads are emulsions of vegetable oils Shortening is rubbing fat into flour, it prevents gluten from being produced and makes pastry and biscuits short - crumbly Saturated fats come mainly from animals sources (e.g meat, butter, suet, dripping lard) are solid or semi solid at room temperature and are associated with high levels of saturated fatUnsaturated fats come mainly from vegetable sources and are usually liquid at room temperature, peanut, sunflower, corn, soya,rapeseed and olive oil -Adding colour, butter in pastry makes it golden yellow-Adding flavour, butter in shortbread and pastry give it a nice flavour Our bodies use fat to make cholesterol, which is an essential part of all cell membranes and its needed to make hormones, however high cholesterol levels are said to increase the risk of heart disease.
|
|
What foods do we get... from and why do we need it: Vitamin AVitamin BVitamin CVitamin DCalciumIron What are micro and macro nutrients?
|
Vitamin A is from retinol and is found in liver, butter, fish oils and eggs. Vitamin A is goos for eyesight and growth and functions of tissuesVitamin B is found in cereals, liver, kidney, peas, pulses, dairy produce meat and fish-B1 thiamin helps the nervouse system and the release of energy from carbs-B2 riboflavin helps with the release of energy and repair of tissues-B3 niacin helps with the release of energy-Folic acid is crucial for growth and important for women planning a preganancyVitamin C is found in citrus fruits, green veg, peppers and potatoes. Its good for protecting the body from infection and allergies, helps in the absoprtion of calcuimVitamin D Found in oily fish and eggs, and is produced by the body when exsposed to sunlight, helps the body absorb calcium a lack of it can lead to rickets and osteoporosisCalcium is found in milk, tofu, salmon, green leafy vegetables, hard water and white bread. Needed for strong bones and teeth and healthy nerves and muscles. Lack of calcium could lead to osteoporosisIron is found in darkk green leafy vegetables and meat. Its needed to form part of the haemoglobin that gives blood cells their red colour. Lack of iron can cause a deficiency called anaemia Micro nutrients are needed in small amounts (vitamins and minerals) Macro nutrients are needed in large amounts (fat, NSP, protein, carbs, fats)
|



