Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Aftershock
|
Vibrations that follow an earthquake
|
 Asthenosphere |
Part of the Earth that lies beneath the lithosphere and consists of fluid-like rock
|
 Caldera |
A large depression formed when a volcano collapses into the empty magma chamber after an eruption
|
 Cinder cone |
A steep slope formed from deposits ejected from a volcano
|
 Composite cone |
Steep slope formed of alternating layers of solid rock and tephra from volcanic eruptions
|
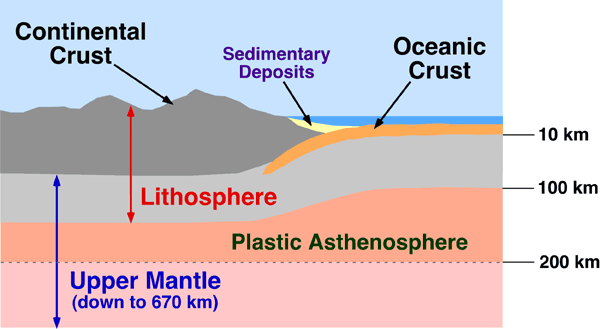 Continental crust |
Landmass material
|
 Continental drift |
Theory that all landmass was once a single continent that broke apart, leading to the relative movement of continents today
|
 Convection current |
Movement of a fluid caused by a difference in temperature
|
 Convergent boundary |
A border between two tectonic plates in which the plates collide with each other
|
|
Crust
|
The outermost layer of the Earth
|
 Density |
Rhe ratio of an object's mass divided by its volume
|
 Divergent boundary |
A border between two tectonic plates in which the plates move away from each other
|
 Earthquake |
Sudden movement of the Earth's crust
|
|
Elastic rebound theory
|
Rheory stating that rocks stressed past their breaking point fracture and release energy as waves
|
 Epicenter |
Point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus of an earthquake
|



