Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Asteroid |
A naturally formed, unevenly shaped, rocky or metallic body in the solar system that is too small to hold an atmosphere
|
|
Astronomical unit (AU) |
Average distance between the earth and the sun, approximately 149.5 million kilometers
|
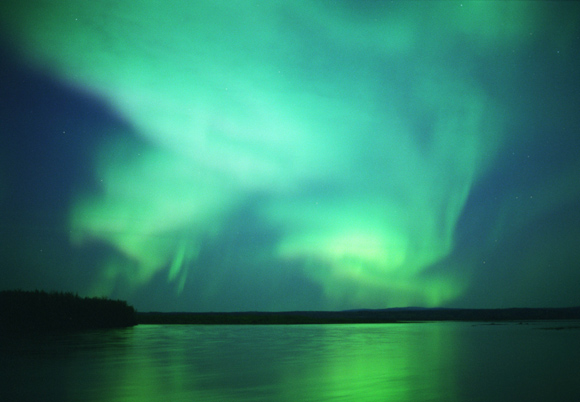 Aurora |
A magnetic storm in the earth's atmosphere that appears as bands of light in the sky
|
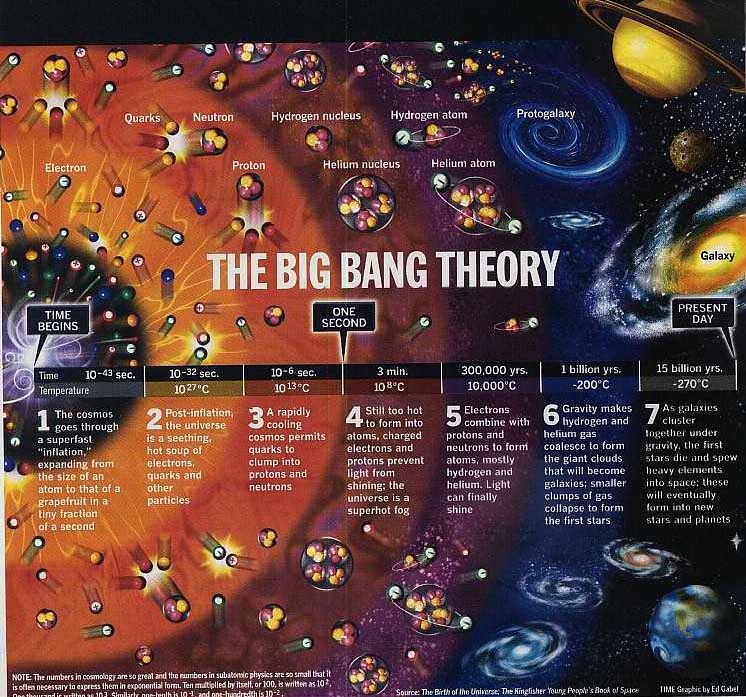 Big Bang theory |
Currently accepted theory of the origin of the universe, stating that
all matter in the universe was once compressed into an infinitely dense
point and then expanded in all directions
|
 Black hole |
An object formed by the collapse of a large star in space with gravity so great that not even light can escape its pull
|
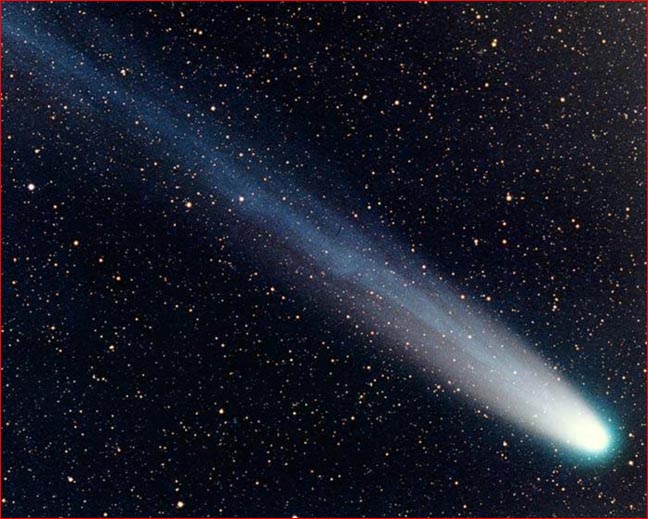 Comet |
A small, irregularly shaped body of solid ice, rock, and iron that orbits the sun in a highly irregular orbit
|
 Constellation |
A region of the sky, usually containing a group of stars thought to form a figure
|
 Electromagnetic radiation |
Waves with electric field and magnetic field components that travel at the speed of light in a vacuum
|
 Dwarf star |
A star with a radius similar to or smaller than the earth's sun
|
 Fusion |
The joining of two atoms to form a more massive one
|
 Giant star |
A star with a radius between 10 and 100 times that of Earth's sun
|
|
Light year
|
The distance that light travels in one year, equal to about 9.5 trillion kilometers
|
 Lunar eclipse |
Event during which the earth comes between the moon and the sun, casting a shadow across the moon
|
 Meteor |
The streak of light in the sky resulting from the intense heating of a meteoroid in a narrow channel in Earth's upper atmosphere
|
 Meteoroid |
A small piece of rock or metal moving through the solar system
|



