Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
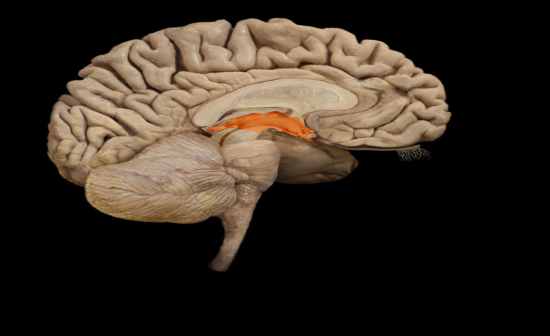 What is this structure? |
Diencephalon
|
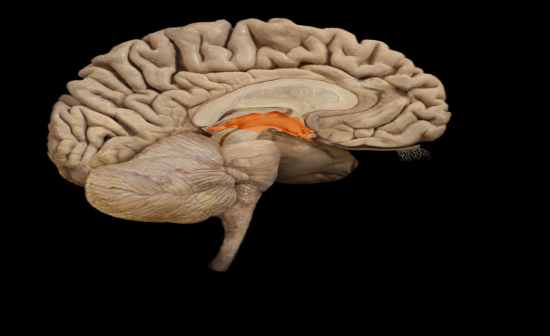 What is the function of the Diencephalon? |
Function:
• Thalamic nuclei relay sensory information to cerebral cortex • Hypothalamic nuclei maintain homeostasis • Epithalamus includes pineal gland (produces melatonin |
 What is this structure? |
Thalamus
|
 What is the function of the Thalamus? |
Function:
• Primarily for relay of sensory information to cortex • Relay of motor information for movement planning |
|
Function:
• Primarily for relay of sensory information to cortex • Relay of motor information for movement planning |
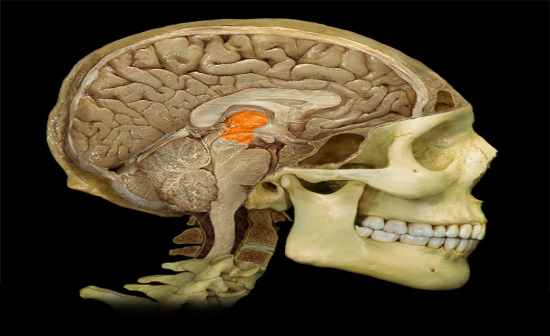 Thalamus |
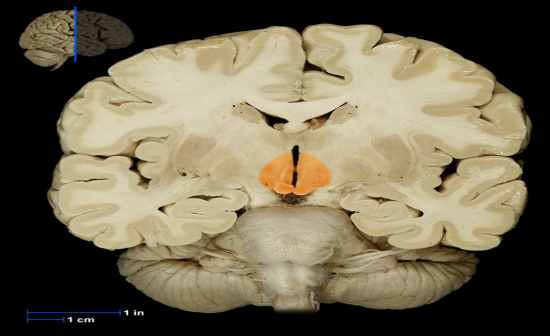 What is this structure? |
Hypothalamus
|
 What is the function of the Hypothalamus? |
Function:
• Considered master control center for endocrine system • Secretes releasing and inhibiting hormones that control anterior pituitary gland • Produces hormones that are transported to and stored in posterior pituitary gland • Controls autonomic nervous system • Regulates body temperature, food, and water intake • Regulates emotional behavior • Maintains sleep/wake cycle |
|
Function:
• Considered master control center for endocrine system • Secretes releasing and inhibiting hormones that control anterior pituitary gland • Produces hormones that are transported to and stored in posterior pituitary gland • Controls autonomic nervous system • Regulates body temperature, food, and water intake • Regulates emotional behavior • Maintains sleep/wake cycle |
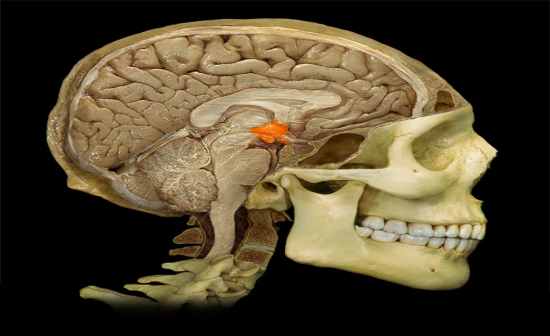 Hypothalamus |
 What is this structure? |
Optic Chiasma
|
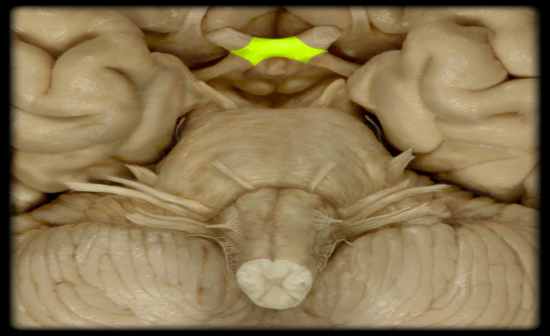 What is the description of the Optic Chiasma? |
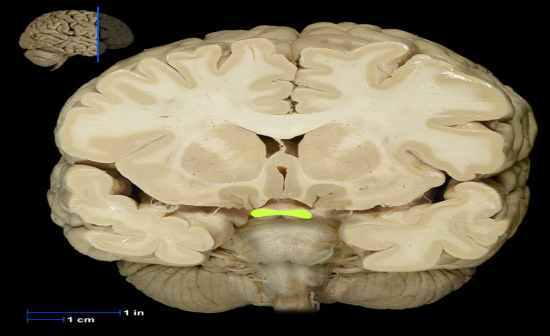 Description: • White matter tract composed of axons of retinal ganglion cells from both eyes traveling to thalamus and other brainstem nuclei • Some axons from each retina decussate (cross) in chiasm to enter opposite optic tract |
|
Description:
• White matter tract composed of axons of retinal ganglion cells from both eyes traveling to thalamus and other brainstem nuclei • Some axons from each retina decussate (cross) in chiasm to enter opposite optic tract |
 Optic Chiasma |
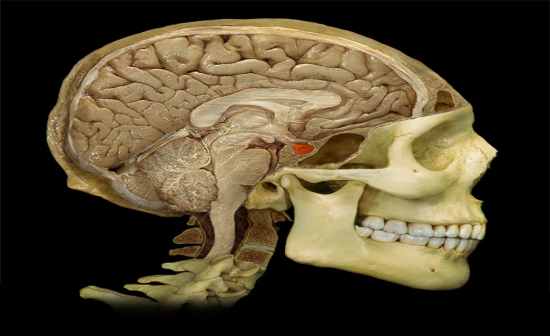 What is this structure? |
Pituitary gland
|
|
Function:
• Anterior pituitary produces the following hormones: thyroid-stimulating (TSH), prolactin (PRL), adrenocorticotropic (ACTH), growth (GH), luteinizing (LH), melanocyte-stimulating (MSH), and follicle-stimulating (FSH) • Posterior pituitary stores and releases: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT) |
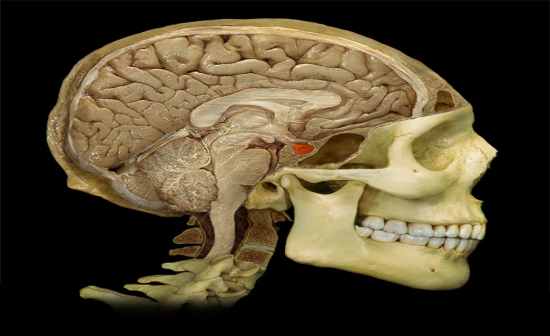 Pituitary gland |
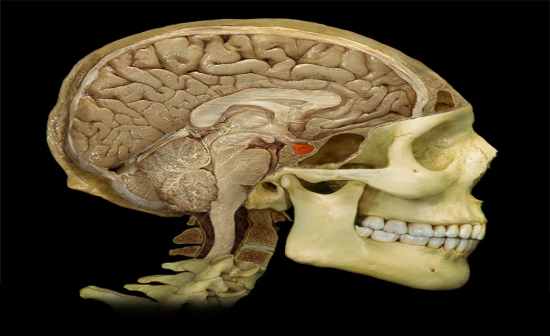 What is the function of the Pituitary gland? |
Function:
• Anterior pituitary produces the following hormones: thyroid-stimulating (TSH), prolactin (PRL), adrenocorticotropic (ACTH), growth (GH), luteinizing (LH), melanocyte-stimulating (MSH), and follicle-stimulating (FSH) • Posterior pituitary stores and releases: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin (OT) |
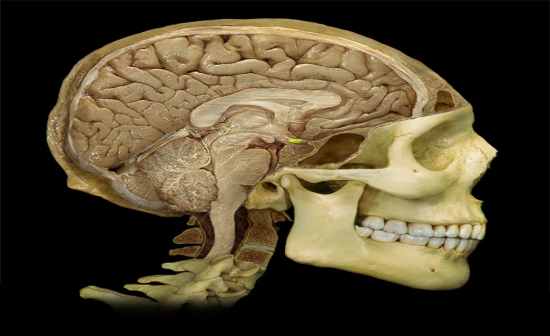
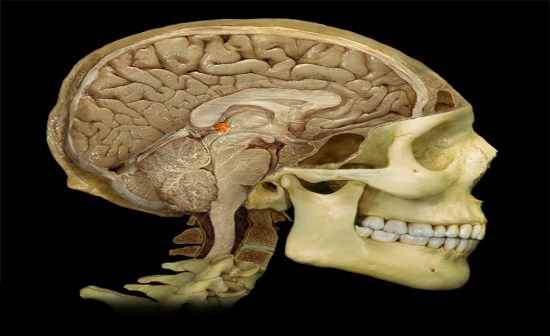 What is this structure? |
Pineal Body
|



