Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Drug eruptions
|
- any medication has the potential to cause an adverse rxn
- common offenders include antibiotics, NSAIDs, anti-hypertensive meds, anti-seizure meds, and Rx pain meds - Morbilliform (maculopapular) rashes and urticarial reactions are the most common drug eruptions - Perform a punch biopsy on an active site to help confirm the diagnosis - send specimen to dermatopathologist - communicated w/physician who prescribed the suspected drug before stopping any medication - recommend a drug be stopped one at a time for 4-6 weeks to see if rash resolves |
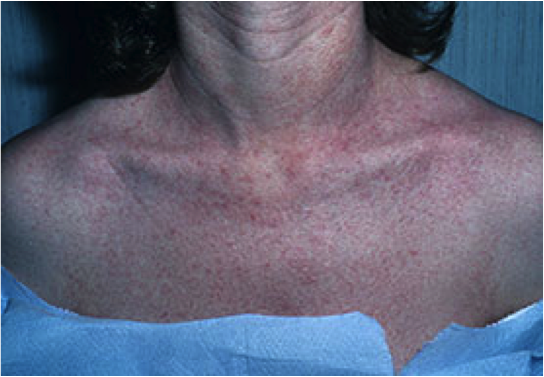 . |
Drug eruptions: Morbillifom
|
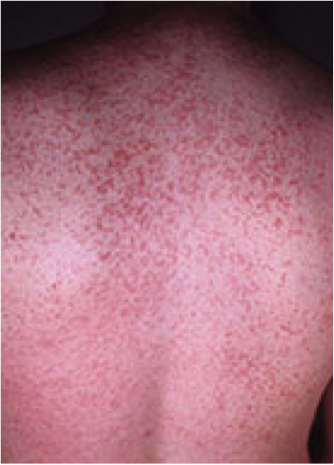 . |
Drug eruption: diffuse
|
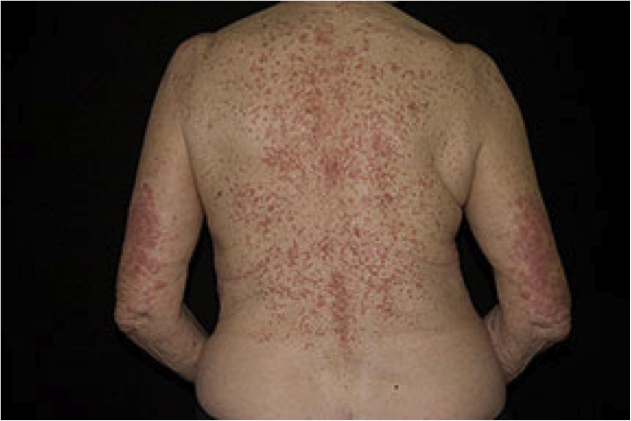 . |
Drug eruption: diffuse
|
 . |
Drug eruption: urticarial
|
 . |
Drug eruption: vesicles
|
 . |
Drug eruption: photodermatitis
|
|
Common causes of drug reactions
|
- antibiotics: PCN, Sulfas, cephalosporins
- diuretics: photosensitivity drug rxns ex. HCTZ - NSAIDs: fixed drug eruption, vasculitis - Anticonvulsants: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome |
 . |
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (Erythema Multiforme Major) with mucocutaneous involvement
Will present with widespread rash and lesions in eyes, mouth, and nose. |
|
Therapy for Drug Eruptions
|
- Discontinue the offending drug
- Antihistamines for pruritis - Short course of prednisone tapered if necessary - Moisturizers to reduce infection - Oral or topical antibiotics if suspect secondary infection from scratching |
|
Viral Exanthems
|
- Common childhood diseases
(usually benign and go away on their own, with only some exceptions) - Vaccinations important for reducing epidemics (MMR) - Usually preceeded by a prodrome of fever and constitutional symptoms |
|
What is the common presentation of Measles (rubeola)?
|
- Prodrome: 3 C's
1. cough 2. coryza (head cold) 3. conjunctivitis Also will have fever, fatigue, and arthralgias |
|
,
|
Measles (rubeola)
|
|
How soon does the measles rash start?
|
Rash begins 3-4 days
|
|
.
|
Measles (rubeola)
|



