Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are the main functions of the cytoskeleton? (3)
|
-cell scaffolding- shape cells- driving force behind cell movement
|
|
What are the 3 major components of cytoskeletons?
|
Intermediate filaments, microtubules, microfilaments
|
|
What is the width of microfilaments?
|
7-11nm
|
|
What is the width of microtubules?
|
25nm
|
|
What is the width of microfilaments?
|
5nm
|
|
Which cytoskeleton component has a coiled coil structure?
|
Intermediate filaments
|
|
Explain each of the following with respect to IFs:-composed of____
-stability ____-where they're found ___ |
- fibrous polypeptides in an alpha helical rod (a dimer)- relatively stable- different types are associated with different cells, but they are all specific to that cell
|
|
How can we use microfilaments for research purposes?
|
For typing of cells
|
|
Name the 4 types of IFs, the monomers that fall into each of those groups, and where each of those are found.
|
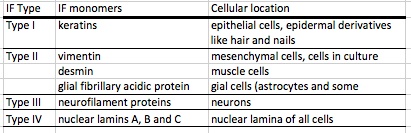 . |
|
Explain the structure of IFs
|
There are alpha helical dimers, four of which line up to form a tetramer. Tetramers aggregate end-to-end to form a protofilament. 8 protofilaments make a 10nm thick IF. Globular domains project from the surface and account for variations between individual types of intermediate filaments
|
|
Protofilament
|
Type of intermediate filament that is composed of 4 intermediate filament dimers (a tetramer).
|
|
The main function of IFs is to ______
-how? |
Maintain cell structure
- they extend from the nuclear envelope to the plasma membrane. Keratin filaments form a network that crisscrosses the interior of the cell and attach to the spot desmosomes. |
|
As far as construction of IF goes, there is no evidence for ________
|
Rapid polymerization or depolymerization
|
|
IFs are common in what cells?
|
- cells subject to mechanical stress, epithelial and cardiac muscle cells
|
|
Microtubules are composed of _____
|
Alpha and beta tubulin which form a hollow single microtubule
|



