Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Refer to the exhibit. What statement describes the DR/BDR relationship of the HQ router? • HQ is the DR. • HQ is the BDR. • HQ is a DROTHER. • HQ is a member of an NBMA network |
HQ is a DROTHER.
|
|
Which two features are associated with Frame
Relay OSPF point-to-multipoint environments? (Choose two.)
• A DR is not elected. • The OSPF priority value determines the active DR on the Frame Relay link. • OSPF neighbor routers are statically defined. • The link types are identified as broadcast multiaccess. • The BDR will have a router ID whose value is greater than the DR router ID. |
• A DR is not elected. • OSPF neighbor routers are statically defined. |
 Refer to the exhibit. How was the OSPF default gateway entry for R2 determined? • Default routes are automatically injected by OSPF into all advertisements. • A static default gateway route is defined in the configuration of R2. • The default-information originate command is applied on R1. • The ISP defines the gateway of last resort and automatically passes it to R1 and R2. • The ip default-gateway command is applied on R2 |
• The default-information originate command is applied on R1.
|
|
What is always required for OSPF routers to
share routing information?
• designated routers • a backup designated router • neighbor adjacencies • an NBMA network topology • links that are configured on the 224.0.0.0 network |
• neighbor adjacencies
|
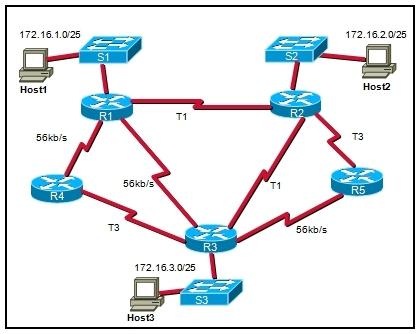 Refer to the exhibit. A network administrator has implemented OSPF and the network has converged. If all router interfaces are enabled and functional, what route will OSPF view as lowest cost when moving frames from Host3 to Host1? • R3 to R4 to R1 • R3 to R1 • R3 to R2 to R1 • R3 to R5 to R2 to R1 |
• R3 to R2 to R1
|
 Refer to the exhibit. Which commands configure router A for OSPF? • router ospf 1 network 192.168.10.0 • router ospf 1 network 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 area 0 network 192.168.10.192 0.0.0.3 area 0 • router ospf 1 network 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192 network 192.168.10.192 255.255.255.252 • router ospf 1 network 192.168.10.0 area 0 |
• router ospf 1
network 192.168.10.64 0.0.0.63 area 0 network 192.168.10.192 0.0.0.3 area 0 |
|
Refer to the exhibit. Which network statement
configures the home router to allow all the interfaces to participate in OSPF?
• network 10.0.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0 • network 10.8.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 • network 10.8.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0 • network 10.10.0.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 • network 10.12.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0 |
• network 10.8.0.0 0.3.255.255 area 0
|
|
Which statement is true regarding OSPF DR and
BDR elections?
• A new DR/BDR election occurs each time a new OSPF neighbor is added. • The router with the highest OSPF priority setting wins the election for DR. • The default priority value for a router connected to a multi-access network is 0. • The router with the highest MAC address is elected as the DR when the default priority values are used. |
• The router with the highest OSPF priority setting wins the election
for DR.
|
|
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator
would like only the 172.16.32.0 network advertised to Router1. Which OSPF
network command accomplishes this?
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.15 area 0 • Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.0.0 0.0.15.255 area 0 • Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.32.0 0.0.15.255 area 0 • Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.32.0 0.0.255.255 area 0 |
• Router2(config-router)# network 172.16.32.0 0.0.15.255 area 0
|
|
Which two
statements describe the operation of link-state routing protocols? (Choose
two.)
• All routers in the same area have identical link-state databases when converged. • Routing loops are prevented by running the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL). • Link-state routers send frequent periodic updates of the entire routing table. • Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) is used to deliver and receive LSAs. • Calculating the shortest path for each destination is accomplished with the SPF algorithm. |
• All routers in the same area have identical link-state databases when
converged.
• Calculating the shortest path for each destination is accomplished with the SPF algorithm. |
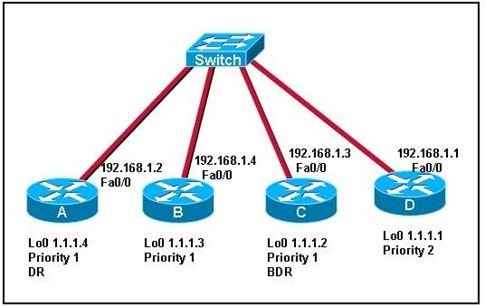 Refer to the exhibit. Routers A, B, and C are part of the existing OSPF network. Router D has been added to the network. All routers are running OSPF and have the indicated priorities applied to the interface. What is the DR/BDR status immediately after router D is added to the existing network? • An election is forced and router D wins the DR election. • The DR and BDR do not change until the next election. • An election is forced and the existing BDR becomes the DR. • The router with the highest router ID becomes the new BDR. |
• The DR and BDR do not change until the next election.
|
|
Which two statements describe the use of OSPF
DR/BDR elections? (Choose two.)
• Elections are always optional. • Elections are required in all WAN networks. • Elections are required in point-to-point networks. • Elections are required in broadcast multiaccess networks. • Elections are sometimes required in NBMA networks. |
• Elections are required in broadcast multiaccess networks.
• Elections are sometimes required in NBMA networks. |
 Refer to the exhibit. As part of an OSPF network, R1 and R2 are trying to become adjacent neighbors. Although it appears that the two systems are communicating, neither of the routing tables include OSPF routes received from its neighbor. What could be responsible for this situation? • R1 and R2 are not on the same subnet. • The Process IDs on each router do not match. • The timer intervals on the routers do not match. • The value set for the Transmit Delay time on both routers is too low. |
• The timer intervals on the routers do not match.
|
 Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the value 128 shown in bold? • It is the OSPF cost metric. • It is the OSPF administrative distance. • It is the value assigned by the Dijkstra algorithm that designates the distance in hops to the network. • It is the value assigned to an interface that is used by the DUAL algorithm to determine the metric. |
• It is the OSPF cost metric.
|
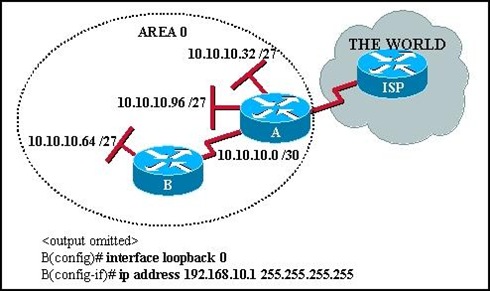 Refer to the exhibit. What is the purpose of the configuration commands added on router B? • allows router A to form an adjacency with router B • provides a stable OSPF router ID on router B • provides a method of testing router traffic • creates the OSPF adjacency table on router B |
• provides a stable OSPF router ID on router B
|



