Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Atom (2)
|
-Building blocks of matter
Made of 3 types of particles1. Protons in nucleus (+ charge)2. Neutrons in nucleus (neutral charge)3. Electrons around nucleus (negative charge) |
|
Proton (2)
|
Has positive charge combines with neutron to make most of atomic mass
|
|
Solution
|
Homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances
|
|
Solute
|
The substance being dissolved (usually a solid)
|
|
Solvent
|
The substance doing the dissolving (usually a liquid)
|
|
Molarity (aka)note Formula
|
# moles of solute in one Litre of a solution
(aka M) note: the volume must always be in liters when calculating molarity 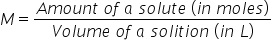 OR: OR: 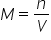 |
|
Why is temperature important to consider when calculating volume of a solution?
|
The volume of a solution may be affected by temp. changes. if temp changes the volume might change too.
|
|
When 2 solutions mix, the volumes may not be ________. Give an example of what ____ means.
|
Additive. i.e. while mixing two 50mL solutions, the final solution might not be a total of 100mL
|
|
Dilution When diluting a solution, the number of moles of the solvent DOES/DOESN'T change. Formula
|
The process of reducing concentration of a solution either by adding a solute or another solvent. The # moles of the solvent DOES NOT change when diluting a substance(as long as a reaction doesn't take place)
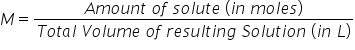 |
|
Density Formula
|
The mass of a unit of volume of the solution
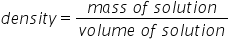 |
|
Parts per Million
Formula VS Parts per Billion |
Ppm- The ratio of mass of a solute to the mass of solution expressed in the same units and multiplied by 106
 ppb- The ratio of mass of a solute to the mass of solution expressed in the same units and multiplied by 109 |
|
What is the molarity of 350 mL solution which contains 25.00g CuSO4?
What are the steps to solve this question? (3) |
1. Find the MM of CuSO4
MM=249.17 g mol -1 2. calculate n (number of moles per CuSO4)  3. Now answer the question by calculating the molarity of the solution: 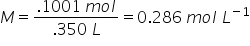 |
|
A solution of HCl has a concentration of 1.258 mol/L. What volume of this solution contains .258 mol of HCl?
|
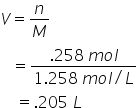 Therefore 205 mL of solution contains .258 mol HCl |
|
A useful relation when comparing between the molarities of the starting and diluted solutions ca be:
note: |
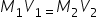 note: this expression explains the fact that the amount of solute before and after dilution with a solvent (or another nonreactive substance) is the same |
|
How well are you going to do on this midterm??
|
SOOO well!! Keep up the great work. It'll be worth it
|



