Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Bonding electrons interact with what types of electromagnetic radiation?
|
Ultraviolet and Visible
|
|
What effect studied by Millikan and Einstein lead to the idea that light can also be treated as a photon (packet of light) rather than a wave?
|
- Photoelectric effect
- E = hv (look at chapter 6 for more information if needed) |
|
Show the difference between reflection and refraction of light.
|
 |
|
Show an example of constructive and an example of destructive interference of two waves.
|
 - Constructive interference: waves are added together - Destructive interference: waves cancel each other out |
|
What is the difference between a continuum and a line source?
|
- Continuum sources usually work on principle of blackbody radiation. Any object > O K gives off radiation. The intensity and wavelength are dependent on temperature.
- Line sources: hollow cathode lamps - used in atomic absorption. Cathode made of a specific metal, low intensity, emission of a specific wavelength. - A continuum uses blackbody radiation and a line source does not. Also, a continuum source is dependent on temperature when it comes to intensity and wavelength and the line source does not. |
|
Give 3 examples of light sources used in spectroscopic instruments and label each source as continuum or line.
|
- Tungsten - continuum
- D2 (Deuterium) - continuum - High pressure Hg or Xe- continuum - Low pressure Hg - line |
|
What are some benefits of lasers?
|
- High intensities
- One wavelength (narrow bandwidth) - Coherent output: all waves are the same frequency and phase - Have very specific wavelengths (relates to bandwidth) so the light does not widen over a long distance, but instead stays in a small straight line. |
|
Draw a picture, labeling all parts, of a grating monochrometer.
|
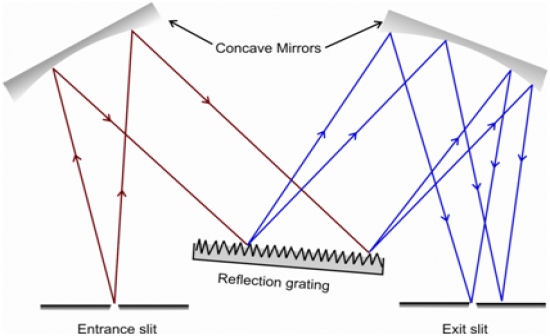 |
|
Define bandwidth.
|
Bandwidth is how wide a wave is or how many wavelengths a certain wave covers.
|
|
Calculate the resolution of a monochrometer that can separate 299 nm light from 302 nm light.
|
R = wavelength/delta wavelength = 299 nm/ 3 nm = 99.7
|
|
What cuvette material would be appropriate to use for a spectrophotometric measurement of 250 nm light? Why?
|
- Quartz would be the appropriate cuvette material to use for a spectrophotometric measurement of 250 nm light because quartz covers 200 - 2000 nm.
- Quartz is relevant to the needed wavelength. |
|
What is the difference between a photon and a heat detector?
|
- A photon detector measures the pulse or electrical current of each individual photon, while a heat detector measures the average signal of all the photons.
|
|
List 3 ideal qualities of a radiation detector.
|
- High signal to noise ratio
- High sensitivity (detect small amounts of light) - Fast response time - constant wavelength response - no signal when not illuminated: no dark current - signal directly porportional to radiant power |
|
Explain how a photomultiplier tube works.
|
- The cathode releases an e- when illuminated.
- The e- then goes to the dynode and is multiplied. Every time the e- (or electrons) hit another dynode, they are multiplied again. There are ten dynodes in total. - All of the electrons will go to the anode. There will be about 106 to 107 e- when they reach the anode. - Fast response time - Sensitivity is limited by dark current |
|
What is a fiber optic cable and how can they be useful in spectroscopic instruments?
|
- A fiber optic cable is a thin strand of plastic or glass that is coated with a layer of plastic or glass (glass with glass, plastic with plastic) that has a refractive index lower than the main material.
- They can be useful in spectroscopic instruments because they can cover farther distances and they do not heat up. (double check in book and quiz though) |



