Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
(Pheomelanin) is the natural pigment in hair that provides:
pronounced: (fee-oh-MEL-uh-nin) |
red to blonde color
From the text: Pheomelanin (fee-oh-MEL-uh-nin) provides natural hair colors from red and ginger to yellow/blonde tones. |
|
Pityriasis capitis simplex is marked by:
|
dry dandruff
From the text: Pityriasis capitis simplex (KAP-ih-tis SIM-pleks) is the technical term for scalp inflammation marked by dry dandruff, thin scales, and an itchy scalp. The scales are usually attached to the scalp in masses or scattered loosely in the hair. Occasionally, the scales are so profuse that they fall to the shoulders. Dry dandruff is often the result of a sluggish scalp caused by poor circulation, lack of nerve stimulation, improper diet, emotional and glandular disturbances, and poor personal hygiene. Treatments include the use of mild or medicated shampoos, scalp treatments, regular scalp massage, daily use of antiseptic scalp lotions, and medicated scalp ointments. |
|
Side bonds account for the hair's:
|
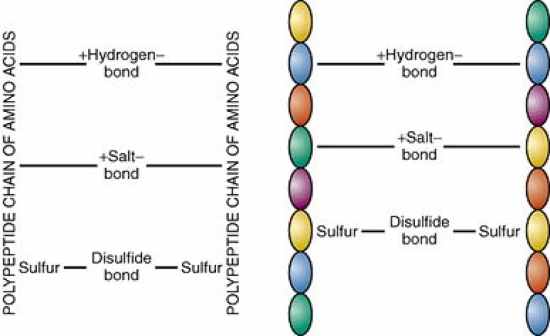 elasticity From the text: The cortex, middle layer of the hair, is made up of millions of polypeptide chains. These polypeptide chains are cross-linked together, like a ladder, by three different types of side bonds: hydrogen bonds, salt bonds, and disulfide bonds. These side bonds hold the hair fibers in place and account for the incredible strength and elasticity of human hair. These side bonds are essential to wet sets, thermal styling, permanent waving, and chemical hair relaxing (see Chapter 15). |
|
A condition characterized by alternating bands of gray and pigmented hair along the hair strand is called:
|
ringed hair
From the text: Ringed hair is a variety of canities, characterized by alternating bands of gray and pigmented hair throughout the length of the hair strand. |
|
Swelling the hair and raising the cuticle layer allows:
|
 liquids to penetrate From the text: A lengthwise section of hair shows that although the cuticle scales overlap, each individual cuticle scale is attached to the cortex. These overlapping scales makes up the cuticle layer. When viewed in cross-section, the scales can be seen to overlap, but it is important to note that hair has only one cuticle layer. Swelling the hair raises the cuticle layer and opens the space between the scales, which allows liquids to penetrate. If there were more than one cuticle layer and they were stacked on top of each other, nothing would be able to penetrate the hair. |
|
Finasteride is a prescription drug that is taken:
|
orally
From the text: Finasteride is an oral prescription medication for men only. Although finasteride is more effective and convenient than minoxidil, possible side effects include weight gain and loss of sexual function. Women may not use this treatment, and pregnant women or those who might become pregnant are cautioned not to even touch the drug because of the strong potential for birth defects. |
|
The dermal papilla contains the blood and nerve supply that provides:
|
nutrients
From the text: The dermal papilla (puh-PIL-uh) is a small, cone-shaped elevation located at the base of the hair follicle that fits into the hair bulb. The dermal papilla contains the blood and nerve supply that provides the nutrients needed for hair growth. |
|
Almost 40 percent of both men and women show some degree of hair loss by age:
|
35
From the text: Androgenic alopecia (an-druh-JEN-ik) or androgenetic alopecia (an-druh-je-NET-ik) is the result of genetics, age, and hormonal changes that cause miniaturization of terminal hair, converting it to vellus hair. Androgenic alopecia can begin as early as the teens and is frequently seen by the age of 40. By age 35, almost 40 percent of both men and women show some degree of hair loss. |
|
Telogen is the:
pronounced: (TEL-uh-jen) |
resting phase
From the text: The telogen (TEL-uh-jen) or resting phase is the final phase in the hair cycle and lasts until the fully grown hair is shed. The hair is either shed during the telogen phase or remains in place until the next anagen phase, when the new hair growing in pushes it out. |
|
Women normally have more than men.
|
vellus hair
From the text: Vellus or lanugo (luh-NOO-goh) hair is short, fine, and downy. Vellus hair is not pigmented and almost never has a medulla. It is commonly found on infants and can be present on children until puberty. On adults, vellus hair is usually found in places that are normally considered hairless (forehead, eyelids, and bald scalp), as well as nearly all other areas of the body, except the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. Women normally retain 55 percent more vellus hair than men. |
|
In general, coarse hair has:
|
the largest diameter
From the text: Coarse hair texture has the largest diameter. It is stronger than fine hair, for the same reason that a thick rope is stronger than a thin rope. Coarse hair also has a stronger structure. It usually requires more processing than medium or fine hair and may also be more resistant to that processing. It is usually more difficult for hair lighteners, haircolors, permanent waving solutions, and chemical hair relaxers to penetrate coarse hair. |
|
A furuncle is an acute, localized bacterial infection of a:
|
hair follicle
From the text: A furuncle (FYOO-rung-kul) or boil is an acute, localized bacterial infection of the hair follicle that produces constant pain. It is limited to a specific area and produces a pustule perforated by a hair. |
|
The pigment in the cortex that gives natural color to the hair is known as:
|
melanin
From the text: All natural hair color is the result of the pigment located within the cortex. Melanin (MEL-uh-nin) is the tiny grains of pigment in the cortex that give natural color to the hair. The two different types of melanin are eumelanin and pheomelanin. |
|
Fatty (greasy or waxy) dandruff scales that mix with sebum and stick to the scalp in patches or crusts are characteristic of:
|
pityriasis steatoides
From the text: Pityriasis steatoides (stee-uh-TOY-deez) is a scalp inflammation marked by fatty (greasy or waxy) types of dandruff. Greasy or waxy scalp scales mix with sebum and stick to the scalp in patches or crusts. Constant itching may cause the person to scratch the scalp. If greasy scales are torn off, bleeding or oozing of sebum may result. A client with this condition should be referred to a physician for medical treatment. |
|
Hydrogen, salt, and disulfide bonds are:
|
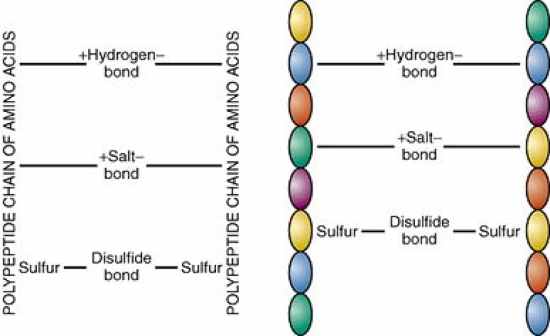 side bonds From the text: The cortex, middle layer of the hair, is made up of millions of polypeptide chains. These polypeptide chains are cross-linked together, like a ladder, by three different types of side bonds: hydrogen bonds, salt bonds, and disulfide bonds. These side bonds hold the hair fibers in place and account for the incredible strength and elasticity of human hair. These side bonds are essential to wet sets, thermal styling, permanent waving, and chemical hair relaxing (see Chapter 15). |



