Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Lacks true tissues (but several types of cells)
Sedentary Hermaphrodite |
Sponges
|
|
Collar Cells supporting the structure
Forms gametes |
Choanocytes
|
|
Resides in the mesohyl (gelatinous region, eggs)
Transport nutrients to other cells |
Amoebocytes
|
|
Both sessile and mobile (2 body plans)
Hydras, corals, jellies Carnivorous Have contractile tissues and nerves (no brain) Radial Symmetry Gastrovascular cavity One opening 4 classes: Hydrozoa, Scyphozoa, Cubozoa, Anthozoa |
Cnidarians
|
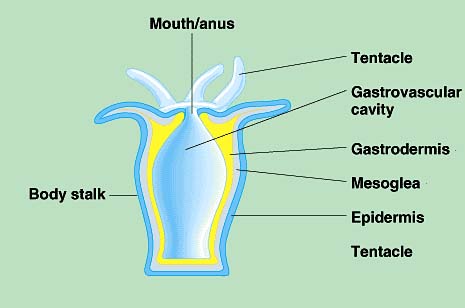 See Picture |
Cnidarians Stationary body plan (Polyp)
|
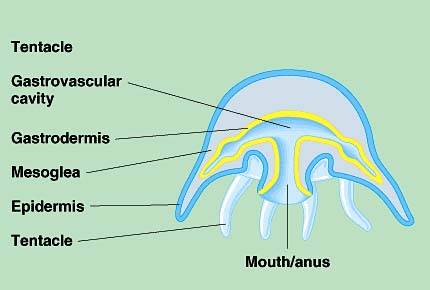 See Picture |
Cnidarians Motile body plan (Medusa)
|
|
Specialized stinging thread (cnidarians only)
For capturing prey |
Nematocyst
|
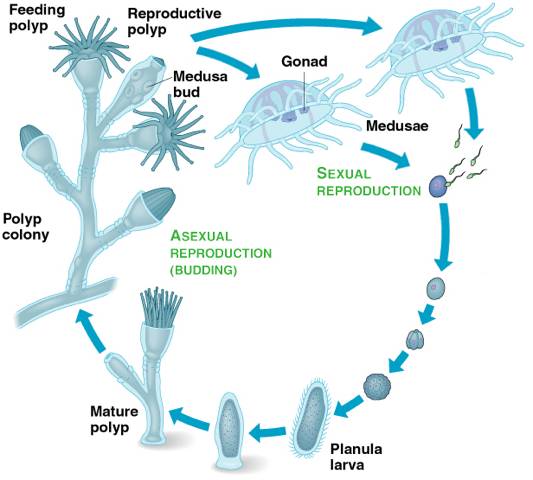 Both freshwater and marine Alternate between medusa polyp |
Cnidaria - Hydrozoans
|
 Mostly medusa Coastal at polyp stage Open ocean at medusa stage |
Cnidaria - Scyphozoans
|
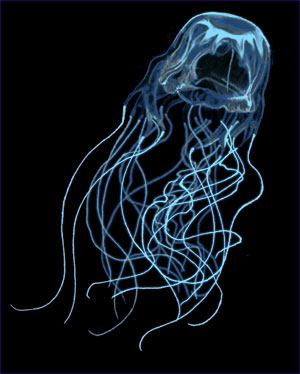 Box-shaped medusa stage Eyes embedded fringe Strong Swimmer Tropical Ocean Highly toxic cnidocytes |
Cnidarian - Cubozoans
|
|
Polyps
Sea anemone and coral Solitary or colonial (colonial = hard exoskeleton) |
Cnidarian - Anthozoans
|
|
Have 18 phyla
Most diverse group of body plans Bilateral, coelomates Lophophore (feeding) Trochophore (larval stage) 6 main phyla: flatworms, rotifers, ectoprocts, brachiopods, molluscs, annelids |
Lophotrochozoans
|
|
Marine, freshwater, damp terrestrial
Free living and parasitic Thin, dorsoventrally flattened Acoelomates Simple excretory system Protonephridia (flame cells fro osmotic regulation) |
Lophotrochozoans - Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
|
|
Free living
Mostly marine Freshwater - planarians Swim with cilia or muscles Light sensitive eyespots Later flap (detect chemicals) Nervous system (complex, centralized) Hermaphrodites |
Lophotrochozoans - Platyhelminthes - Tubellarians
|
|
Parasitic
Suckers to attach to host animal Reproductive organs majority of inside Asexual/sexual reproduction |
Lophotrochozoans - Platyhelminthes - Monogeneans/Trematodes
|



