Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Solstice
|
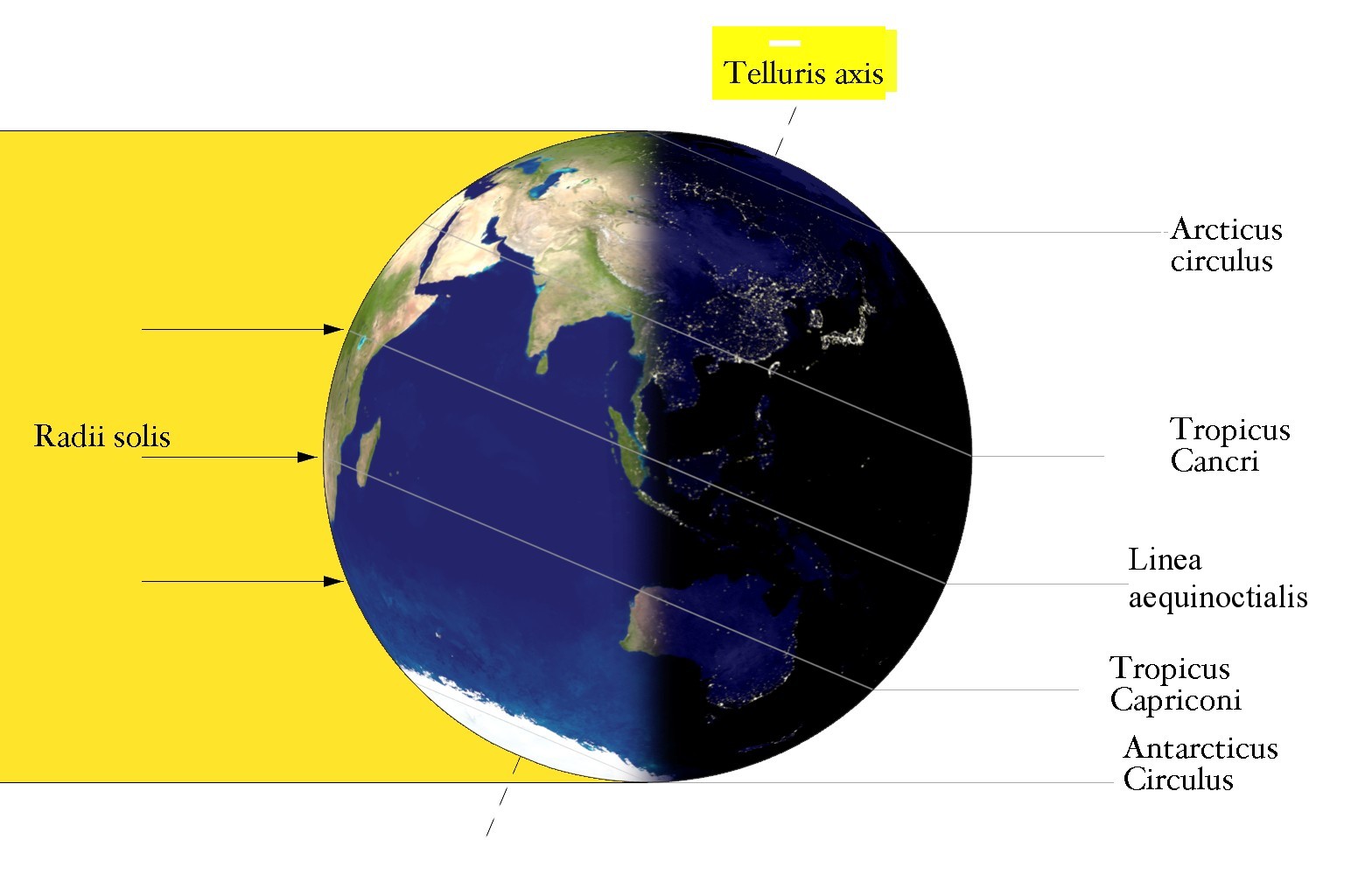 Either of two times of year when the sun's rays shine directly overhead at noon at the furthest points north or south, and that mark the beginning of summer and winter. |
|
Equinox
|
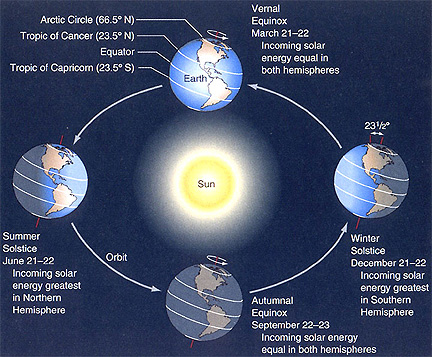 Each of the two days in a year on which day and night are equal in length; marks the beginning of spring and autumn. |
|
Weather
|
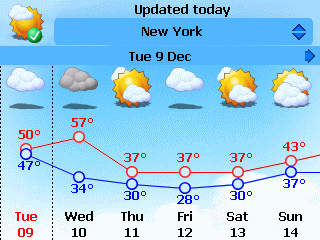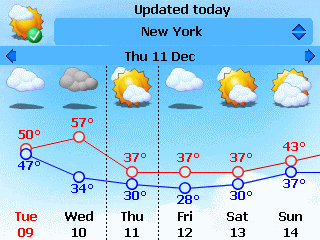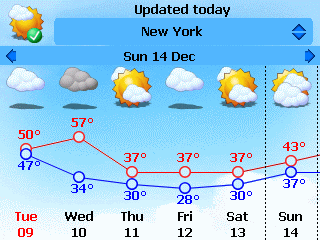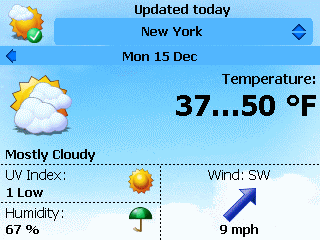 The condition of the atmosphere at a particular location and time. |
|
Climate
|
 The typical weather conditions at a particular location as observed over time. |
|
Precipitation
|
 Falling water droplets in the form of rain, sleet, snow, or hail. |
|
Rain Shadow
|
 The land on the leeward side of hills or mountains that gets little rain from the descending dry air. |
|
Hurricane
|
 A storm that forms over warm, tropical ocean waters. |
|
Typhoon
|
 A tropical storm, like a hurricane, that occurs in the western Pacific. |
|
Tornado
|
 A powerful funnel-shaped column of spiraling air. |
|
Blizzard
|
 A heavy snowstorm with winds of more than 35 miles per hour and reduced visibility of less than one-quarter mile. |
|
Drought
|
 A long period without rain or with very minimal rainfall. |
|
Convection
|
 The transfer of heat in the atomsphere by upward motion of the air. |
|
El Nino
|
 Is a natural change in the climate. |
|
Greenhouse Effect
|
 The layer of gases released by burning of coal and petroleum that traps solar energy, causing global temperature to increase. |
|
Tundra
|
 Flat treeless land forming a rung around the arctic circle. |



