Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Superpowers |
United States and Soviet Union
|
 Cold War |
(Struggle between United States and the Soviet Union) differences political beliefs and policies soon pulled two superpowers apart
|
 Bipolarism |
Idea of two superpowers for the idea that they two will put the world in jeapordy
|
 Security Council |
Assigned bulk of power by the UN charter provided for six major bodies (has 11 members)
|
 United Nations |
Headquartered in New York City. Permanent international organization. The purpose was to maintain peace by guaranteeing the security of member nations
|
 General Assembly |
Assigned a bulk of power by the UN charter provided by six major bodies (policy making body)
|
 Economic and Social Council |
3rd body, oversaw fights against poverty, ignorance and disease
|
 International Court of Justice |
4th body, handled international legal disputes
|
 Trusteeship Council |
5th body. promoted the welfare of people in colonial territories and helped them toward self rule
|
 Secretariat |
6th body. handled the UN's administrative work
|
 "debating society" |
Known for the UN becoming deadlocked
|
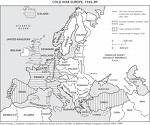 "iron curtain" |
Referred to the Soviet. made barrier split Europe into non-communist Western Europe and Communist Eastern Europe
|
 George Kennan |
Presented ideas for new policy and he is a state department expert on Soviet Union. suggest policy of containtment
|
 Containment Doctrine |
Applied for the first time in the Eastern Mediterranean. held back the spread of communism
|
 Truman Doctrine |
The foreign policy by President Truman. U.S. took on international responsibilities as the leader of Western World
|



