Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What is stress? What are the factors that determine how
we experience potentially stressful events?
|
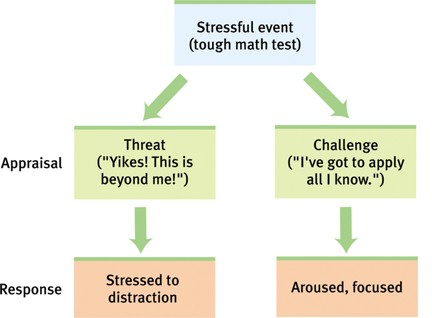 A process by which we perceive and respond to certain events, called STRESSORS, that we appraise as threatening or challenging. - our response depends on how we appraise the event |
|
What is our physiological
response to stress? In particular,
what is the “fast response” and the “slow response” and what specific hormones
are involved?
|
- the Sympathetic Nervous System cause the Adrenal gland to release cortisol (slows down) and epinephrine and norepinephrine (speed up)
|
|
What is Selye’s general
adaptation syndrome (GAS), and how
does it explain the effects of prolonged stress? (See Figure 12.23)
|
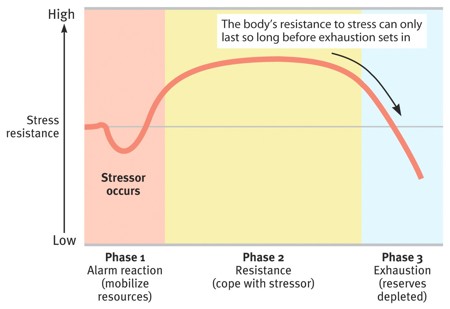 Concept of the body's adaptive response to stress in 3 phases: ALARM, RESISTANCE, EXHAUSTION - prolonged stress caused long term effects on our health as well. Stress can cause cell death and age and early death... :O |
|
What are the 3 general
types of categories of stressful life events?
|
1. Catastophic Events 2. Life Changing Events3. Daily Hassles
|
|
What did Weiss’s 1977 study
of rats tell us about the role of perceived control in stressful situations? (See Figure 12.30) What about optimism vs. pessimism?
|
 - the rat that gets shocked randomly gets stressed out, and is more likely to develop ulcers. The rat that is under-control of the shock and can turn it off is just as healthy as the rat that doesn't get shocked!!!! - lack of perceived control over stressful events leads to more severe health consequences. |
|
How does poverty and
inequality contribute to stress in a society?
|
 People in more egalitarian (believing all people are equal) society live longer. <3 |
|
What are the goals of behavioral
medicine and health psychology?
|
Bm GOAL: interdisciplinary field that applies behavioral and medical knowledge to health and disease
hp GOAL: subfield of psychology that contributes to behavioral medicine |
|
What are the primary causes
of death in today’s society, and how do they compare to the previous century?
|
Lifestyle related causes: heart disease, cancer, strokes, chronic lung disease... :(
deaths have risen over the last century from these causes... :( |
|
What is coronary heart
disease and how does it relate to stress?
What did Friedman & Rosenman’s study on male personality types
(i.e., Type A and Type B) tell us about stress and heart disease?
|
- the clogging of blood vessels that nourish the heart- influenced by stress and personality: A and B
Type A= competitive, hard-driving, verbally aggressive, anger-proneType B= easy going, relaxed people |
|
How does stress influence
the immune system?
|
PSYCHONEUROIMMUNOLOGY: the suppression on lymphocytes makes us susceptible to illness, and exacerbates the progress of AIDs and Cancer boooooo....
|
|
What are some of the major
factors that can reduce or help us cope with stress? In particular, what is biofeedback, and what is meant by social support?
|
aerobic exercise- helps alleviate depression and anxiety
Biofeedback is electronic feedback regarding a physiological state (bp, muscle tension) and allows the control of physiological responses to stress through relaxation techniques. Social Support is the degree of social interaction with others, and of personal satisfaction from relationships. (STRONG social support counteracts the effects of stress.) |
|
How might spirituality
and religious practice help us cope with stress? In particular, what are some of the important correlates to
religious activity that might explain the beneficial effects on health? (See Figure 12.36)
|
 People that go to church are part of a community. Therefore, they have social support, healthy behaviors, and positive emotions, and so they tend to live LONGER! |
|
What is alternative medicine? Why should one be cautious about
believing the health claims of alternative medicine?
|
-commercially available healthcare treatments that are NOT used in hospitals, reimbursed by insurance companies, adequately tested, widely taught at med schools, SHOULD NOT BE ALWAYS TRUSTED. - perceived effects may be due to spontaneous remission
|



