Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Describe the lesion. What are 4 differentials for this disease? |
Nasal erosions, nasal ulceration
Bovine papular stomatitisBVDVFMDVVesicular stomatitis |
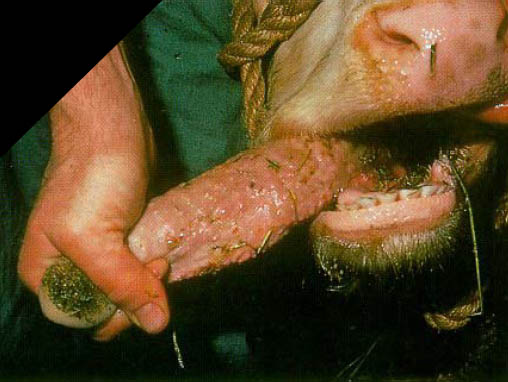 1. What is this disease commonly called? 2. What is the causative agent? 3. Describe the lesions. 4. How does the cow contract this agent? 5. What do you treat it with |
1. Wooden tongue
2. Actinobacillus lignerasia 3. Gritty, granulomatous abscesses, hard diffuse nodular swellings on tongue 4. Plant awns/stems -> mucosal damage -> bacteria into tissue. 5. Na Iodide IV (s/c dilute lots - irritant) |
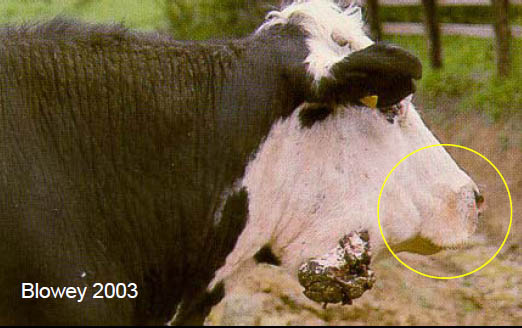 1. What is this disease commonly called? 2. What is the causate agent? 3. Describe the lesions 4. How does the cow contract this agent? 5. How do you diagnose? 6. How do you treat it? |
1. Lumpy jaw
2. Actinomyces bovis 3. Hard immovable mass, non-painful, fibrotic, sometimes exudative. 4. Lesion in skin/mucosa, bacteria enter and multiply -> periosteal new bone and fibrosis. 5. Squash prep of exudate -> gram +ve rods, clinical signs (hard immovable mass) 6. Can't really treat it.. Just limit spread/arrest lesions. Na Iodide, ?penicillin? |
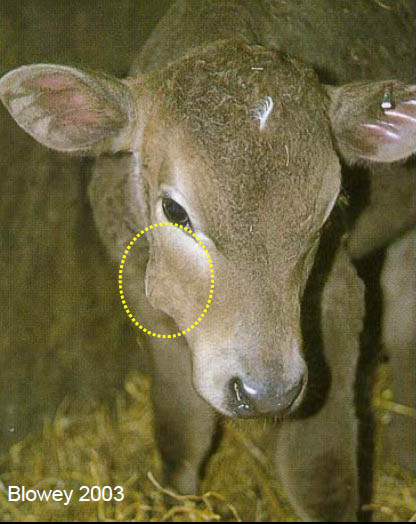 1. What is this disease? 2. What is the causative agent? 3. What ages are normally associated with this disease? 4. How does it invade? 5. How to treat? |
1. Oral Necrobacillosis
2. Fusobacterium necrophorum 3. 2 weeks - 3 months. 4. Mucosal injury -> opportunistic invader 5. Parenteral antibiotics - TMS |
 1. What is the handler showing? 2. How is this remedied? |
1. Oesophageal obstruction
2. Sedation + deep internal palpation -> remove obstructionMassage externally, pass tube if too far in and flush (with head DOWN to prevent aspiration) |
 1. What % dehydration would this calf be and why? 2. What are some possible ddx for this calf? |
1. - recumbant, depressed, unkempt coat- can't see eyes (?sunken?) or know about suckling reflex.
- probably ~8% 2. E. coli, rotavirus, salmonella, coronavirus (less common), coccidiosis |
 What does this kit test for? |
- Coronavirus- E. coli- Rotavirus- Cryptosporidia
|
 1. What are some ddx for this calf? 2. Would you use antimicrobials? |
1. Salmonella, rotavirus, coronavirus (less commonly reported)
2. Yes - mucosal damage -> septicaemia more likely- Ceftiofur 10mg/kg 2x per day. IM or IV. |
 What neurological disease might this calf have? |
- Bacterial meningitis- Viral meningitis
|
 1. Describe what is going on with this cow. 2. DDx? |
1. Abdominal distension, both R) and L)
2. Frothy bloat, abomasal impaction, obstruction, vagus indigestion, ascites |
 1. What is this picture showing you? 2. How could this happen? |
1. "bloat line" area cranial (or caudal depending on aetiology) is congested whereas the opposite end is ischaemic causing a line to form
2. frothy/gas bloat, PM change (due to post mortem bloating) |
 What is this image displaying? What sequelae may happen? |
Hardware (nails, wire, metal objects) in reticulum. Can cause Traumatic Reticuloperitonitis
|
 1. What is this cow showing? 2. DDx? |
1. Signs of abdominal pain - hunched back, reluctance to move
2. - Traumatic Reticuloperitonitis- Peritonitis- Intussusception- Volvulus- Displaced abdominal contents (e.g. LDA/RDA) |
 1. What is this picture showing? 2. DDx? 3. Tx? |
1. Malaena
2. - Small intestinal/abomasal ulceration with associated bleeding.- Abomasal volvulus 3. Conservative - change diet to hay and treat with antacids +/- blood transfusion |
 What pathological process would you expect to auscultate here? |
Left displacement of abomasum
|



