Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
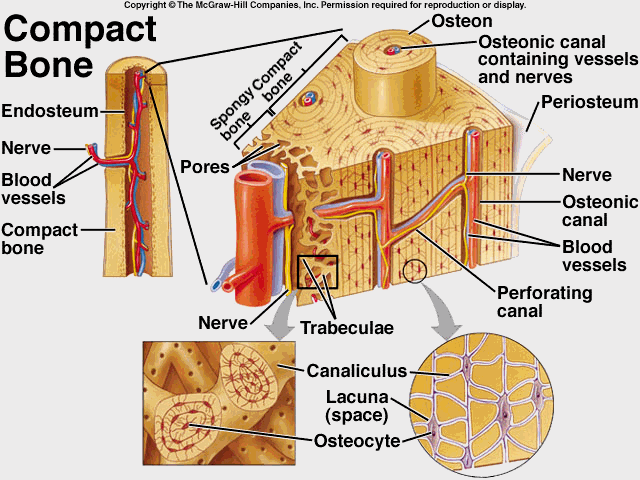
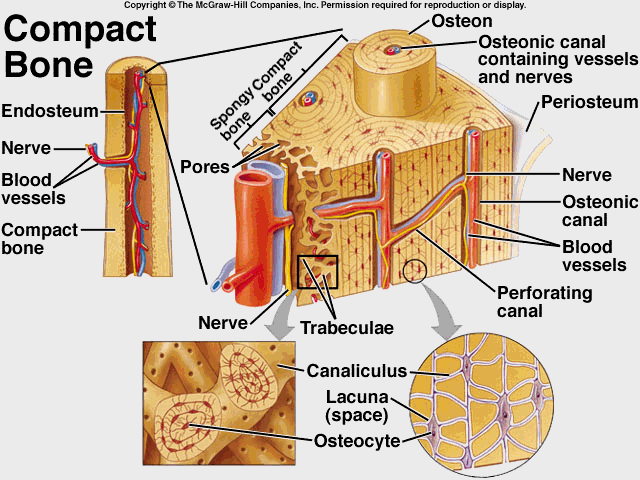 Haversian Canal System |
 |
|
An easy way to remember the work of osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes is
|
Osteoblasts giveth.
Osteoclasts taketh away. Osteocytes maintaineth. |
|
Osteoblasts
|
Osteoblasts are the builders and make collagen and hydroxyapatite. Some of the
osteoblasts become buried in their matrix and then they are referred to
as osteocytes. The rest of the osteoblasts cover the new bone's surface. Waves of osteoblasts that move into the area form new layers of bone.
|
|
Osteoclasts
|
Osteoclasts are larger cells whose function is to dissolve bone by acting on the mineral matrix. They make enzymes such as collagenase, which breaks down collagen. Osteoclasts also secrete various acids that can dissolve the hydroxyapatite structure.
|
|
Osteocyte
|
After
the osteoblasts are buried in bone, they're referred to as osteocytes.
Osteocytes account for 90 percent of all cells in the skeleton
|
|
Calaliculi
|
Osteoblasts change their shape and become buried in their matrix, connected to each other only by thin processes called canaliculi
|
|
Parathyroid
|
Regulation of calcium metabolism
|
|
Calcitonin
|
Inhibits bone removal by osteoclasts, and promotes bone formation by osteoblasts
|
|
Compact Bone
|
Compact bone is the hard material that makes up the shaft of long bones and the outside surfaces of other bones
|
|
Spongy Bone
|
Spongy bone consists of thin, irregularly shaped plates called trabeculae, arranged in a latticework network.
|
|
Diaphysis
|
The diaphysis, or shaft, is the long tubular portion of long bones. It is composed of compact bone tissue.
|
|
Epiphysis
|
The epiphysis (plural, epiphyses) is the expanded end of a long bone.
|
|
Metaphysis
|
The
metaphysis is the area where the diaphysis meets the epiphysis. It
includes the epiphyseal line, a remnant of cartilage from growing bones.
|
|
Medullary Cavity
|
The
medullary cavity, or marrow cavity, is the open area within the
diaphysis. The adipose tissue inside the cavity stores lipids and forms
the yellow marrow.
|
|
Articular Cartilage
|
Articular cartilage covers the epiphysis where joints occur.
|



