Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
The change in genetic material of a population of organisms through successive generations; emergence of new species
|
Evolution
|
|
Group of inter-breeding organisms of a particular species; consist of all members of the same species that live in one location
|
Population
|
|
The various alleles of all the genes in all the individuals for one population; can be described in terms of allele frequencies
|
Gene pool
|
|
The gene pool of a population
|
Allele frequencies
|
|
P2+2pq+q2=1
p=dominant allele (A)
q=recessive allele (a)
p+q=1
p2=frequency of homozygous dominant individuals (AA)
2pq=frequency of heterozygous individuals (Aa)
q2=frequency of homozygous recessive individuals (aa)
|
Hardy-Weinberg equation
|
|
When there are no changes in allele frequency from one generation to the next; evolution does not exist
|
Genetic equilibrium
|
|
1. The population is large enough to be unaffected by random gene changes.
2. There is no gene flow (immigration or emigration).
3. There are no mutations occurring or there is mutational equilibrium.
4. There is random mating.
5. There is no natural selection.
|
Genetic equilibrium requirements
|
|
A change in gene pool that occurs purely as a result of chance; always influences gene frequencies to some degree, no matter how large the population
|
Genetic drift
|
|
Describes the capability of an individual of certain genotype to reproduce, and usually is equal to the proportion of the individual's genes in all the genes of the next generation
|
Fitness level
|
|
A program that simulates the evolution of random-mating populations with two alleles, arbitrary fitnesses of the three genotypes, an arbitrary mutation rate, an arbitrary rate of migration between the replicate populations, and finite population size
|
PopG
|
 |
Genetic equilibrium
|
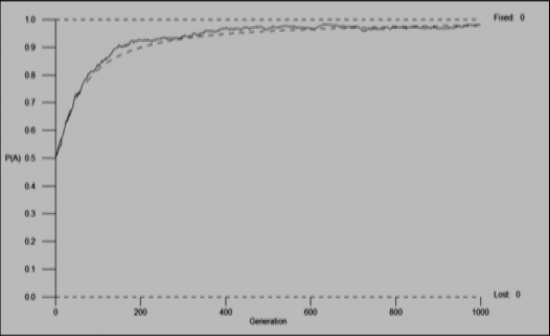 The recessive allele is lost, the frequency of the dominant allele increased |
Selection
|
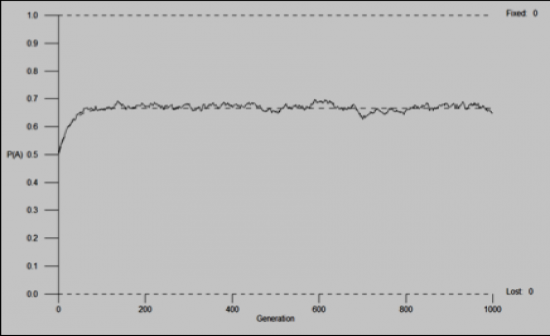 |
Heterozygote Advantage
|
|
Strong effect when the population is small
|
Genetic drift
|
|
Identical copies of a culture on multiple petri dishes in order to test multiple variables/effects on the culture at the same time
|
Replica plating
|



