Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Spell the Phylum
|
Phylum Mollusca
|
|
Widespread in most environments: ____ (all classes), freshwater (some ____ and ___) and even _____ (some gastropods)
|
Marine; gastropods and bivalves; terrestrial
|
|
There are 7 extant molluscan classes, what are they and what do they include in each
|
Bivalvia (clams, mussels), Gastropoda (snails, slugs), Cephalopoda (octopus, squid, cuttlefish, nautilus), Scaphopoda (tusk and tooth shells), Polyplacophora (chitons), Monoplacophora, Aplacophora
|
|
Describe the mollusc ancestry
|
Uncertain but they are protosomes, schizocoelous, and have spiral determinate cleavage
|
|
What are the characteristics of molluscs
|
Triploblastic, organ level organization, bilateral symmetry, eucoelomate but coelom reduced to pericardium and gonadial cavity, protostome, trocophore and veliger larvae as well as some with direct development
|
|
What are the 4 distinct body plan characteristics of molluscs
|
Head, muscular foot (from ventral body wall), visceral mass, and mantle (from dorsal body wall)
|
|
What structures are in the head and foot
|
Sensory organs and muscles
|
|
What structures are in the visceral mass
|
Digestive, reproductive and circulatory organs
|
|
What is the function of the mantle and what does it contain
|
Secretes the shell (if present) and the mantle cavity contains gills or lungs
|
|
What is HAM
|
Hypothetical Ancestral Mollusc=an abstraction derived from comparative morphology and embryology
|
 Find the outer periostracum, prismatic layer, nacreous layers and the free and attached zones of the mantle |
 Find them |
|
How are pearls created
|
Mollusc deposits layers of nacre around an irritant that gets lodged between the mantle and shell
|
|
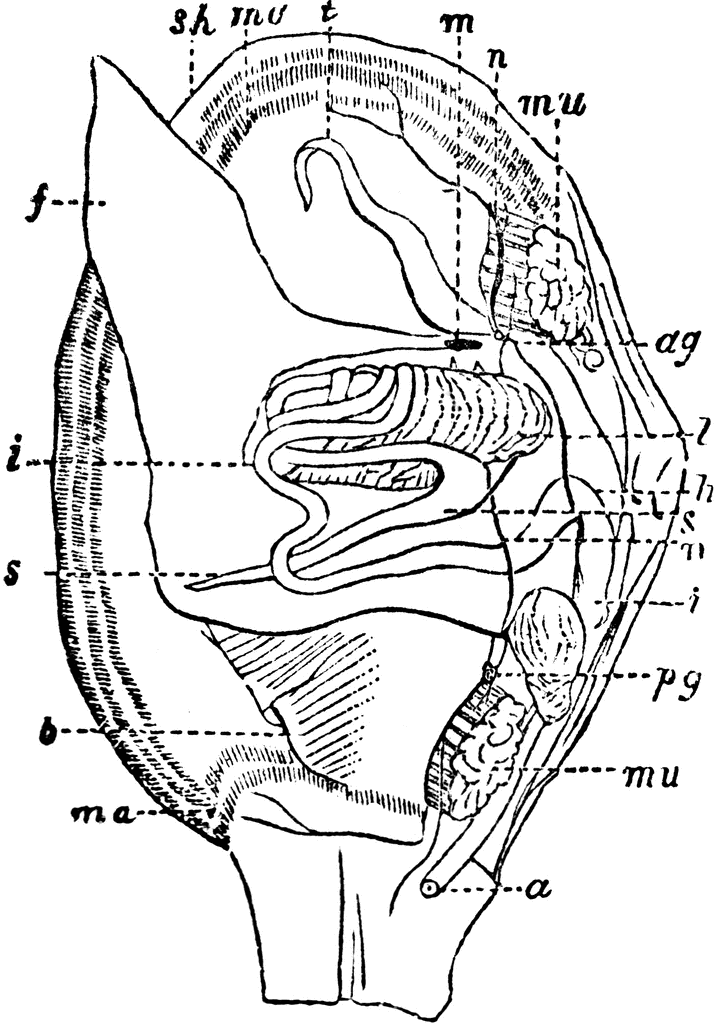
Find the Coelom, mantle, mouth, radula, foot, anus, mantle cavity, gill, and shell |
 Find them |
|
How were each of the molluscan classes derived from HAM
|
Scaphopoda= ventral shell fusion
Gastropoda= torsion of body and coiling of the shell Polyplacophora= shell consists of 8 plates Cephalopoda=lobed foot, highly developed head, shell reduced or lost Bivalvia= bivalved shell, dorsal hinge and adductor muscles |
|
Describe gastropod torsion
|
•
an
unusual developmental process that is peculiar to gastropods and apparently a
primitive feature in this class
• rotation of visceral hump brings mantle
cavity anteriorly - to provide protection to head?
• see a twisting of the visceral mass
through a 180°
rotation during development:
• 1st 90° rotation usually occurs at the
veliger (early larval) stage
• 2nd 90° rotation usually takes longer
and occurs later
|



