Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Passive Transport
|
Movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy from the cell
|
|
Concentration gradient
|
A difference in the concentration of a substance across a space
|
|
Equilibrium
|
Condition in which the concentration of a substance is equal throughout a space
|
|
Diffusion
|
The movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
|
|
Osmosis
|
The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
|
|
Hypertonic solution
|
A solution that causes a cell to shrink because of osmosis
|
|
Hypotonic solution
|
A solution that causes a cell to swell because of osmosis
|
|
Isotonic solution
|
A solution that produces no change in cell volume because of osmosis
|
|
Ion channel
|
Transport protein with a polar pore through which ions can press
|
|
Carrier proteins
|
A protein that transports substances across a cell membrane
|
|
Facilitated diffusion
|
Type of passive transport that moves substances down their concentratino gradient without using the cell's energy
|
|
Active transport
|
The transport of a substance across the cell membrane against its concentration gradient
|
|
Sodium-potassium pump
|
Transports three sodium ions (Na+) out of a cell and two potassium ions (K+) into the cell
|
|
Endocytosis
|
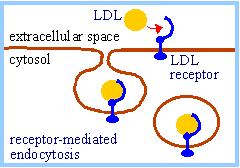 The movement of a substance into a cell by a vesicle |
|
Exocytosis
|
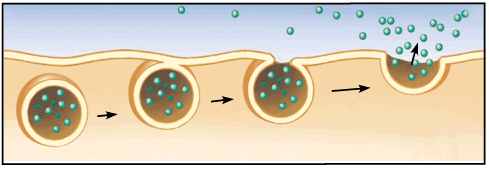 The movement of a substance by a vesicle to the outside of a cell |



