Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
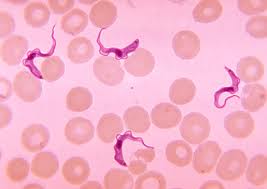 What is the genus, group and clade of this specimen? What disease does it cause? |
Trypanosoma. A kinetoplastid from the Euglenozoa Clade. -Causes African Sleeping Sickness transmitted by the Tse Tse fly. -Kinetoplastids have one large mitochondria.
|
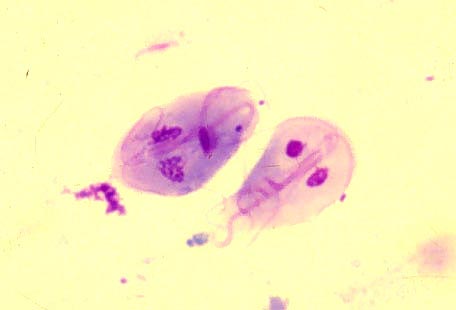 What is this and what disease does it cause? What is the clade and what are two common characteristics of this clade? |
Giardia. From the Diplomonadida Clade. -Has 2 equal-sized nuclei and multiple flagella.-Giardiasis can cause severe diarrhea.
|
 Identify this and from what clade. What disease does it cause? Name a common characteristic. |
Dinoflagellete. From the Alveolata Clade. -Causes "Red tide" and the poisoning associated with it is Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning. -Has two flagella in groove.
|
 What is it? Group? and Clade? Common characteristic? Is it photoautotroph, heterotroph, or mixotroph? |
Euglena. From the Euglenid Group in the Euglenozoa Clade. -It moves in circles and vibrates caused by one or two flagella-They are mixotroph. In sunlight they are autotroph, but when sunlight is unavailable, they become heterotrophic.
|
 Genus? Group? Clade? What disease does is cause? |
Plasmodium spp. From the Apicomplexan Group in the Alveolata Clade. -The parasite is the small purple dot on the red blood cell. -Causes malaria.
|
 Genus? Group? Clade? What does it use for locomotion? |
Paramecium. From the Ciliate Group in the Alveolata Clade. -Uses cilia for locomotion
|
 Identify this organism, its clade, common characteristics. What are the two main functions of pseudopodia? |
Forams. From the Foraminifera Clade. -Have porous shells (aka Tests) that pseudopodia extend from. -Pseudopodia functions in swimming and feeding.
|
|
What is a common characteristic of the Euglenozoa Clade?
|
Have a spiral or crystalline rod inside flagella.
|
|
What is a common characteristic of the Alveolata Clade?
|
Have membrane-bounded sacs (alveoli) just under the plasma membrane,
|
 Identify this and its clade and common characteristic. |
Radiolarians. From the Radiolaria Clade.-Have delicate, intricately, symmetrical internal skeletons made of silica. -Pseudopodia radiate from the central body.
|
|
Identify this and its clade and common characteristic.
|
Amoeba from the Amoebozoa Clade.-Have lobe or tube-shaped pseudopodia
|
|
Identify this example of a cellular slime mold.
|
Sporangia of Dictyostelium.
|
|
What is the function of these stages of the cellular slime mold life cycle?a) Amoeba b) Sporangium
|
A) When food is depleted, hundreds of amoebas congregate to form a slug-like aggregateb) In favorable conditions, amoebas emerge from the spore coats, cells crawl up the stalk and develop spores.
|
|
Identify this example of Plasmodial Slime molds.
|
Physarum. -Plasmodium is the feeding stage.
|
|
Identify this and its clade. What are the cell wall made out of?
|
Diatoms from the Stramenopila Clade.-Cell walls are made of hydrated silica embedded in an organic matrix,
|



