Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Organic Molecules
|
A carbon-containing molecule. Named because they are found in living organisms.
|
|
Macromolecules
|
Many molecules bonded together to form a polymer. Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids (like DNA and RNA)
|
|
Organic Chemistry
|
The study of carbon-containing molecules
|
|
Hydrocarbons
|
Molecules with predominantly hydrogen-carbon bonds
|
|
Summarize the properties that allow carbon to form such a diverse set of organic molecules
|
 Carbon can form both nonpolar and polar bonds, and single and double bonds |
|
Functional Groups
|
A group of atoms with chemical features that are functionally important.
|
|
Some biologically important functional groups that bond to Carbon
|
 |
|
Methyl
|
 CH3: may be attached to DNA, proteins, carbohydrates |
|
Hydroxyl
|
 OH: found in steroids, alcohol, carbohydrates, some amino acids |
|
Carbonyl
|
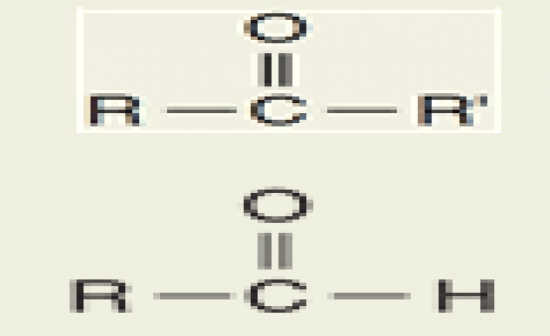 (CO): Steroids, waxes, and proteins |
|
Carboxyl
|
(COOH): amino acids, fatty acids
|
|
Amino
|
(NH2): amino acids (proteins)
|
|
Sulfhydryl
|
(SH) Proteins that contain the amino acid cysteine
|
|
Phosphate
|
(PH4^2-): Nucleic Acids, ATP, attached to amino acids
|
|
Sulfate
|
(SO4-): May be attached to carbohydrates, proteins, lipids
|



