Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Supergroup Chromoalveolata, Group Alveolata
|
Have small internal membrane bound cavities under plasma membrane. monophyletic groupd. som photosynthetic, parasitic, heterotrophic
|
|
Supergroup Chromoalveolata, Group Alveolata,
Subgroup Dinoflagellata
|
Autotrophic or mixotropich. fresh and marine phytoplankton. carotenoid pigments in plastids cause water to be red, produces neurotoxin. most have two flagella, cellulose plates of thecae
|
|
Supergroup Chromoalveolata, Group Alveolata,
Subgroup Dinoflagellata, what species was looked at?
|
 Peridinium |
|
Supergroup Chromoalveolata, Group Alveolata, Subgroup Apicomplexa. What species was looked at? what does its lifecycle llok like?
|
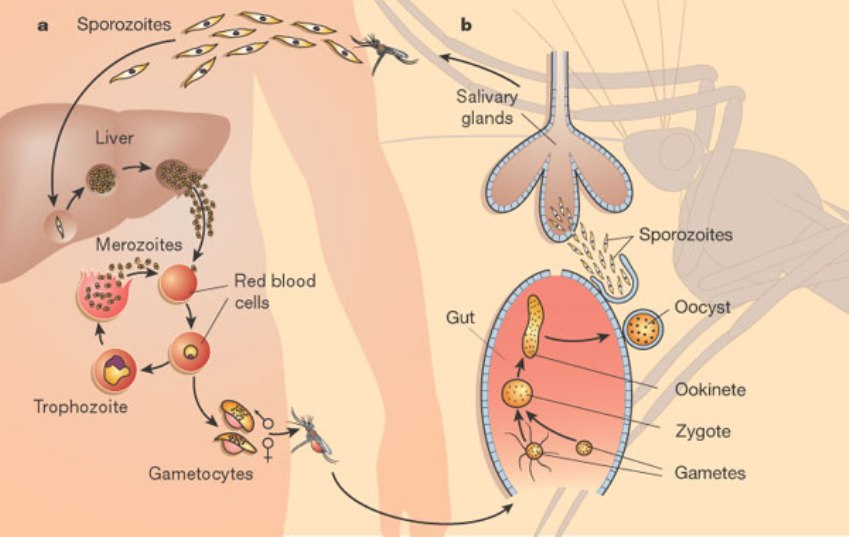 Plasmodium, vector anopholes. looked at blood smear taken from malaria victim. |
|
Supergroup Chromoalveolata, Group Alveolata, Subgroup Ciliophora. What species?
|
 Paramecium. move by cilia. have macronucleus and several micronuclei, reproduce by binary fission asexually. and sexual reprod. for genetic variation>conjugation |
|
What does conjugation look like?
|
 Sexual |
|
What do contractile vacoules of paramecium do?
|
The expel excess water which prevents them from lysing
|
|
Where do food vacoules of paramecium develop?
|
Near lysosomes and on the curve so that food is directed to its mouth at the base of the oral groove. undigested material is expelled out anal pore.
|
|
Supergroup Chromalveolata, Group Stramenopila,
|
-"pila" hair-like projections.
|
|
Supergroup Chromalveolata, Group Stramenopila,
Subgroup Bacillariophyta (diatioms)
|
Most numerous phytoplankton. cell wall has two valves made of silica. form diatomaceous earth
|
|
Diatomaceous earth uses?
|
Tooth paste, facial scrub - silica
|
|
Supergroup Chromalveolata, Group Stramenopila,
Subgroup Phaeophyta (brown algae)
|
Most complex protists. large bull kelp (Nereocystis) have holdfast, stipe, blades
|
|
Supergroup Chromalveolata, Group Stramenopila, Subgroup Oomycota (water moulds). How are they similar and different to fungi?
|
Important decomposers. Saprolegnia ferax. (1)
water mouls have multinucleate filaments (hyphae) that resemble fungi hypahe. (2) heterotrophs (3) molds have centrioles and cellulose and flagella - fungi have chitin
|
|
What protists move using pseudopodia?
|
Foraminferans, radiolarions and amoebozoans
|
|
Supergroup Rhizaria, Group forminifera.
|
Marine, shelled protists. have thin pseodopodia extend from pores (forams). Shells (tests) are multi-chambered contain calcium carbonate. form marine deposits. snail like
|



