Related Flashcards
Related Topics
Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Turbellaria; planarian Dugesia body plan
|
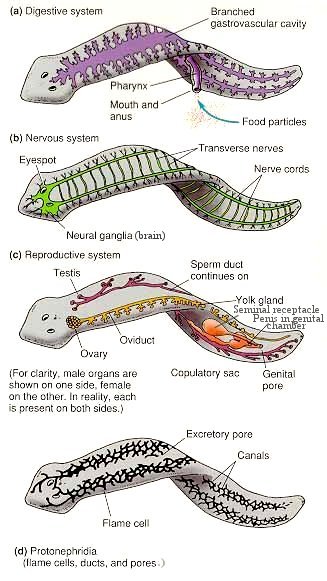 Branching gastrovascular cavity walls of pharynx are muscular. In cross section two white circles for nerve cords |
|
Turbellaria; planarian Dugesia feeding and structure of the Gastrovascular Cavity
|
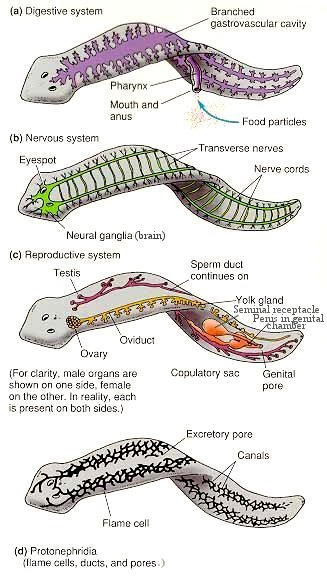 Digestive tract consists of a mid ventral mouth, muscular pharynx and a gastrovascular cavity. Two posteriorly blind-ending branches from the pharyngeal cavity and one anteriorly blind-ending branch. When feeding the pharynx is protruded and applied to the prey (passive feeding). |
|
Turbellaria; planarian Dugesia Excretion and Osmoregulation
|
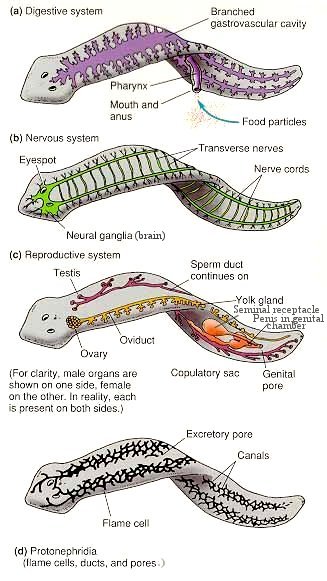 Excretory system consists of branched network of tubules composed of flames cells (with ciliary activity) and excretory canals. |
|
Turbellaria; planarian Dugesia Reproduction
|
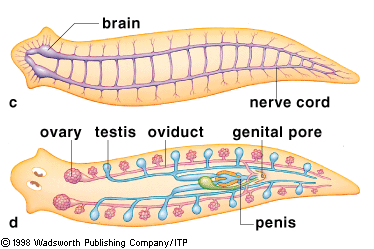 Asexual reproduction (transverse fission, budding can also be seen) rarely sexual reproduction |
|
Trematoda; Diagenea body plan
|
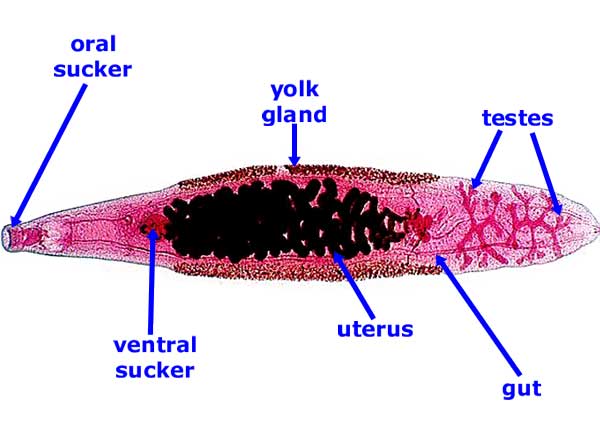 Parasitc flukes as adult body form like leaf Ventral and oral sucker; no dorsal hooks posterior end is blunt Running posteriorly and laterally are the two branches of the gastrovascular cavity. The majority of the tubular network in the center of the body comprises the reproductive system. absence of cilia (differs from turbellaria) |
|
Trematoda; Diagenea feeding
|
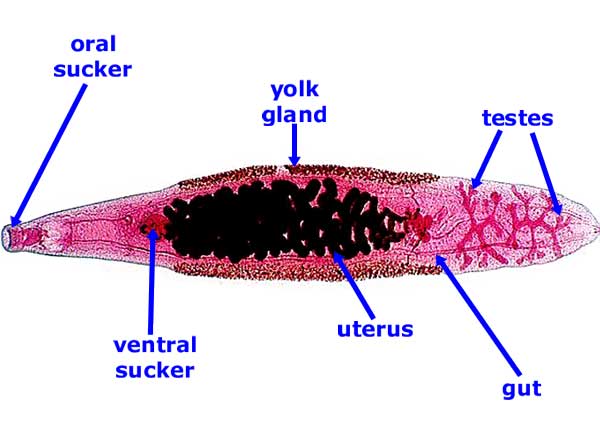 Anterior oral sucker surronds mouth which leads to muscular pharynx and a short esophagus into two blind-ending elongate caeca |
|
Trematoda; Diagenea Excretion and Osmoregulation
|
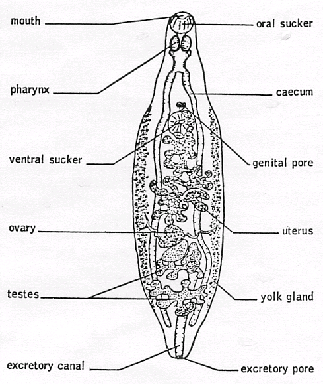 Protonephridial excretory system canals along the side of the body with fine network of flame cells near the ventral sucker lateral excretory trunks run posteriorly and join to form a median duct or bladder which opens ventrally via an excretory pore. |
|
Trematoda; Diagenea Reproduction
|
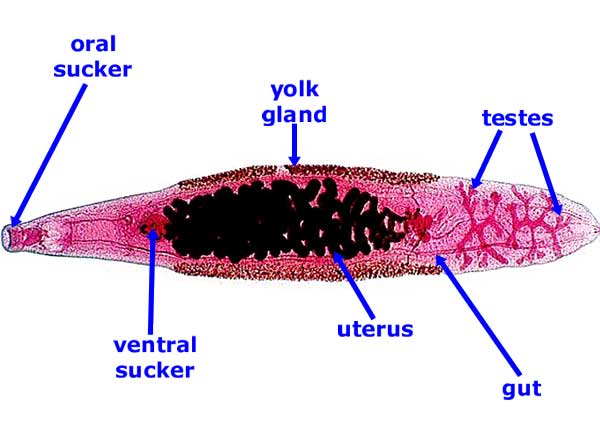 Coiled uterus with many fertilized eggs are stored many exhibit a copulation canal mostly cross fertilization (but can also do self fertilization) |
|
Trematoda; Diagenea life cycle
|
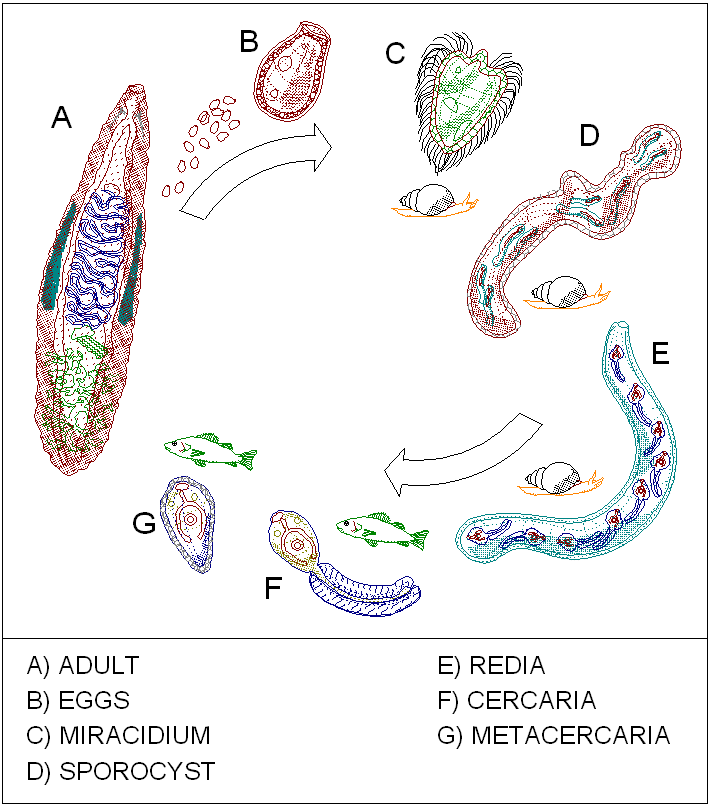 A |
|
Cercomeromorpha; Monogenea body plan
|
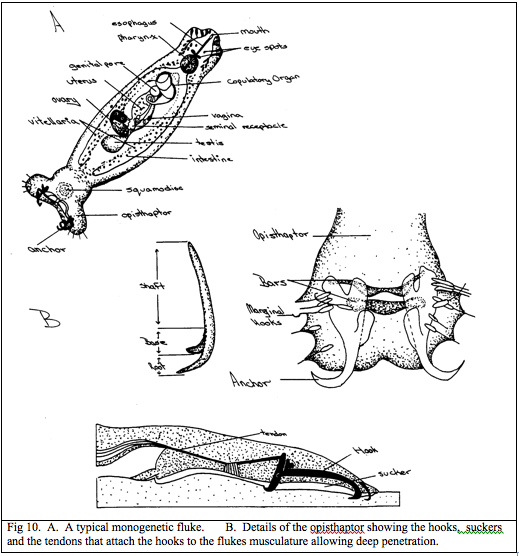 Mostly marine ectoparasitic and flattened body. Similar to Trematoda except: Anchor at Posterior end with barbs and hooks Only one oral sucker and oral hook |
|
Cercomeromorpha; Monogenea life cycle
|
A
|
|
Cercomeromorpha; Cestoda body plan
|
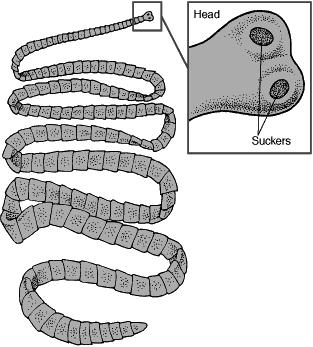 Tape worm with ribbon like form and adults are all endoparasites in the guts of vertebrates Body consists of linear series of proglottids that become progressively smaller, so the most anterior tip of the animal consists of a microscopic pointed scolex. Scolex has hooks and suckers to hold on in the gut; and also buds off proglottids containing male and female reproductive organs. |
|
Cercomeromorpha; Cestoda feeding
|
No gastrovascular cavity. They have a digestive absorptive layer of skin and are completely dependent on the nutrient coming from the host organism.
|
|
Cercomeromorpha; Cestoda excretion and osmoregulation
|
Flame bulbs and scolex and running posterior and lateral excretory vessels
|
|
Cercomeromorpha; Cestoda reproductition
|
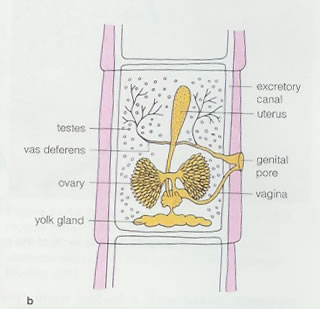 Hermaphrodites and with one set of both reproductive organs in the proglottid. younger proglottides are found near the scolex |




