Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
List and Identify the CRANIAL BONES
|
Bone: Temporal bone
 |
|
What is the External Auditory Meatus?
|
The ear canal which runs from the outer ear to the middle ear.
|
|
Mastoid Process
|
|
|
Styloid Process
|
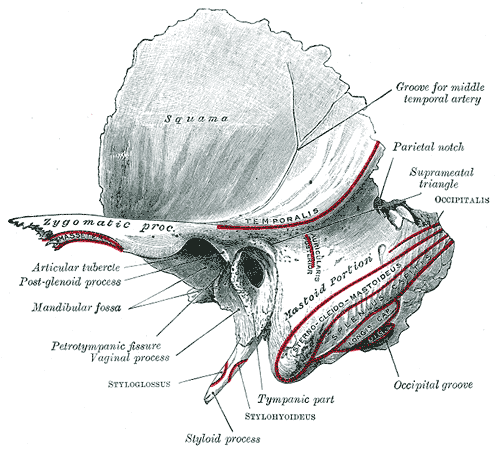
The styloid process is a slender pointed piece of bone just below the ear. It projects down and forward from the inferior surface of the temporal bone, and serves as an anchor point for several muscles associated with the tongue and larynx.
 |
|
Petrous portion of the temporal bone
|
The petrous portion of the temporal bone or pyramid is pyramidal and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital. Directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents for examination a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and contains, in its interior, the essential parts of the organ of hearing.
 |
|
The seven bones that articulate to form the ORBIT
|
The orbital bone is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated.
 The seven bones that articulate to form the orbit.
The seven bones that articulate to form the orbit.yellow = Frontal bone green = Lacrimal bone brown = Ethmoid bone blue = Zygomatic bone purple = Maxillary bone aqua = Palatine bone red = Sphenoid bone |
|
What are the four margins of the orbits and what does each margin contain?
|
The base, which opens in the face, has four borders. The following bones take part in their formation:
|
|
Nasal Bone
|
 |
|
Vomer
|
The vomer is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones
.
 |
|
What is the septum?
|
The two nasal cavities are separated from each other by the nasal septum, a partition in the midsagittal plane.
|
|
What is the function of the Nasal Cavity?
|
The nasal cavities conditions the air to be received by the areas of the respiratory tract and noses. Owing to the large surface area provided by the conchae, the air passing through the nasal cavity is warmed or cooled to within 1 degree of body temperature. In addition, the air is humidified, and dust and other particulate matter is removed by vibrissae, short, thick hairs, present in the vestibule. The cilia of the respiratory epithelium move the particulate matter towards the pharynx where it passes into the esophagus and is digested in the stomach.
|
|
What are the parts of the septum?
|
1. a front part composed of cartilage
2. an upper back part that is the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid (sieve like) bone
3. a lower back part that is the vomer bone.
|
|
What are the functions for LIFE of the upper airway?
|
1. Eating
2. Breathing
3. Vomiting
4. Coughing
5. Sneezing
|
|
What is the function of the upper airway for speech?
|
It is the FILTER FUNCTION. The upper vocal tract modulates shapes of the cavities and spaces and locations of constriction to resonate (enhance) some frequencies of the glottal tone and attenuate (lessen) others.
|
|
Resonate harmonics:
|
Reinforce
|



