Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Describe Lardosis and Kyphosis
|
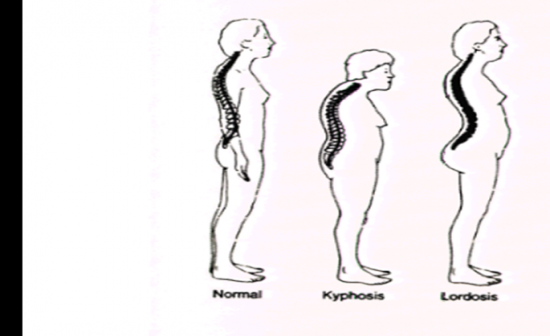 Refer to picture |
|
Describe primary and secondary curvature of the back
|
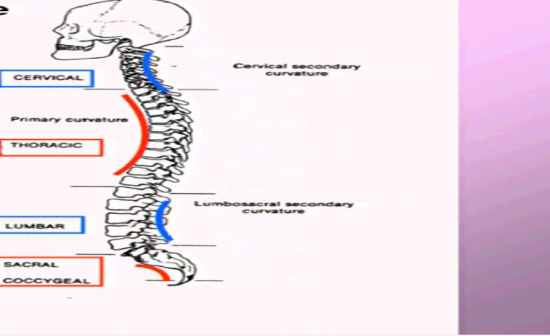 Refer to picture |
|
Name all the parts of the arch regarding the vertrebrate
|
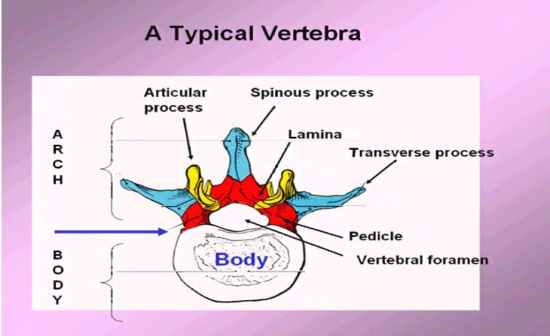 Refer picture |
|
What two places in the spine is there no intervertebral discs and what is there instead
|
The Skull_C1 & C1_C2 they are only reinforced by anterior and posterior longitudinal liguments
|
|
What are the components of the vertebral disks
|
Annulus fibrosis & nucleus pulposus which is self contained fluid-elastic system that can absorb shock and distribute loads over entire surface of body.. make 1/4 of height of adult vertebral colmn
|
|
Wha dictates the type of movents regarding plane the different parts of the spine are able to do?
|
Oreintation of facet junits dictates movements
1. Cervical: oblique/horizontal plane 2. Thoracic: coronal plane 3. Lumbar: Sagittal plane |
|
What region and ligaments support the vertebral column with a lateral view
|
Lateral veiw
Anterior side: anterior longitudinal lig. Posterior side Supraspinous ligament Inters[ompis ligament |
|
When looking at anterior vertreal segments at a posterior view, what will you see?
|
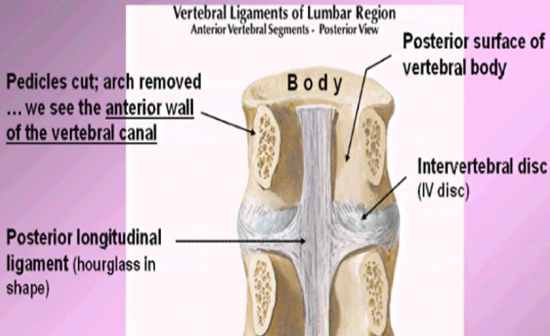 See the posterior longitudinal ligament (hourglass shape) thinner on the sides branching out than in the center. lay over the intervetbral disk |
|
When looking at the Posterior Vewrtebral Segments-Anterior view what would you see with vertebral bodies removed from archs
|
 See the posterior wall of the vertebral canal: showing the ligamentum flavum (yellow) between laminae |
|
How many spinal nerves in relation to spinal cord
Where is the Lumbar Enlargement |
31 pairs of spinal nerves
|
|
What is the conus medullaris and where can it be found? Where does the Dursal Sac end?
|
Conus medullaris is the end of spinal cord found at L2
Dural sac ends at S1 |
|
What is the Cauda Equina and where can it be found
|
Cauda equina (roots of the spinal nerves & filum terminale) start approzimately at the end of L2
|
|
What are the three covers of the spinal cord and the denticulate ligaments
|
Dura covers the spinal cord,
arachnoid is a clear plastic like layer Pie is the deepest layer around spina cord Denticulate ligaments are extensions of pie matter anchord into dura matter |
|
Draw formation of typical spinal nerve, with dorsal ramus, ventral ramus, spinal nerve, lateral cutaneous and anterior curtaneous branch
|
 Refer to pictuer |
|
When looking at the spinal cord in a posterior view, where would the dorsal root gangilio and dorsal roots be?
|
Dorsal root ganglion are little bulbs coming out of the spinal nerves and dorsal root (sensory) are attaching onto the nerve roots which are not covered by Dura mater
|



