Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Gametic life cycle
|
The only haploid cells are the gametes that are produced by meiosis and fertilize to form a
new diploid organism |
|
There are five key
innovations in animal evolution: |
1) The evolution of symmetry - the arrangement of parts either facing each other or around
an axis. 2) The evolution of tissues - tissues allow for specialized structures in animals that have different functions. 3) The evolution of a body cavity - having a body cavity allows for the development and advancement of organs. 4) The evolution of various patterns of embryonic development - allows for differences in body plan. 5) The evolution of segmentation - allows for redundant systems (each segment can duplicate another segment’s functions in case a segment gets damaged) and improved locomotion. |
|
Coelomates
|
Have a coelom that is entirely surrounded by
mesoderm tissue. |
|
Invertebrates
|
Do not have backbones
|
|
Porifera
|
Sponges, lack
symmetry and tissues. |
|
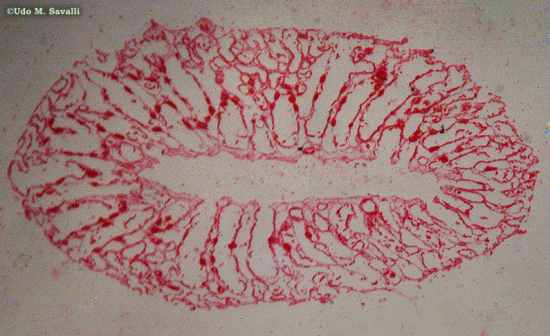
Grantia.
|
 |
|
Grantia.
|
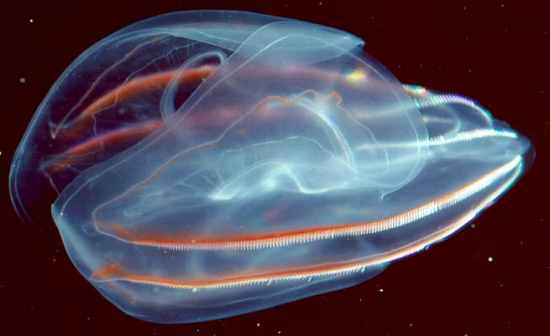
Comb jellies and live in marine habitats. true tissues.
|
|
Comb jellies
|
 |
|
Cnidaria
|
Sedentary and floating organisms
|
|
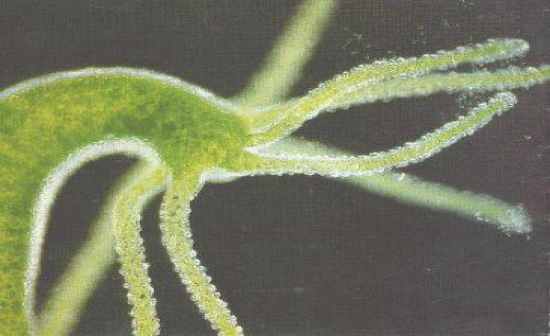
Hydra
|
 |
|
Physalia
|
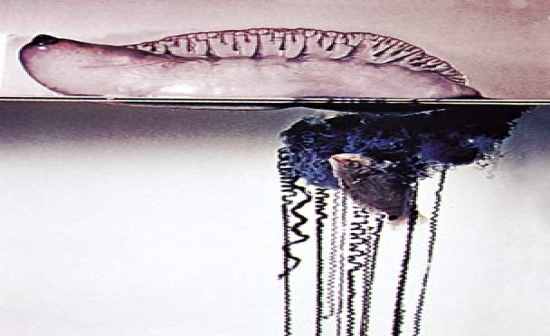 Portuguese man of war |
|
Scyphozoa
|
Medusa stage, jellyfish
|
|
Jellyfish
|
 |
|
Anthozoa
|
Polyp stage, sea
anemones, corals, and sea fans |
|
Metridium
|
 |



