Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
The point of attachment for a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction, Usually the origin lies proximal to the insertion
|
Origin
|
|
Attachment that moves toward the origin during muscle contraction
|
Insertion
|
|
This is the muscle that has the major responsibility for producing a specific movement. Ex: The Biceps Brachii muscle is the PM of elbow flexion
|
Prime Movers (PM) aka Agonists
|
|
Oppose or reverse a particular movement for stability (Useful to reverse a movement), When a PM is active, the antagonist muscles may be relaxed or stretched, These muscles are located on the opposite sides of the joint across which they act.
|
Antagonist
|
|
When a synergist immobolizes a bone, or a muscle’s origin site so that the prime mover has a stable base on which to act, they are called fixators
|
Fixators
|
|
Assist PMs by Adding a extra force to the same movement
and Reducing undesirable or unnecessary movements that might occur as the prime mover contracts. Ex: The finger flexor muscles cross both the wrist and the interphalangeal joints, but you can make a fist without bending your wrist because of synergistic muscles stabalizing the wrist. |
Synergists
|
|
Pectoralis Major: location, action, origin, insertion
|
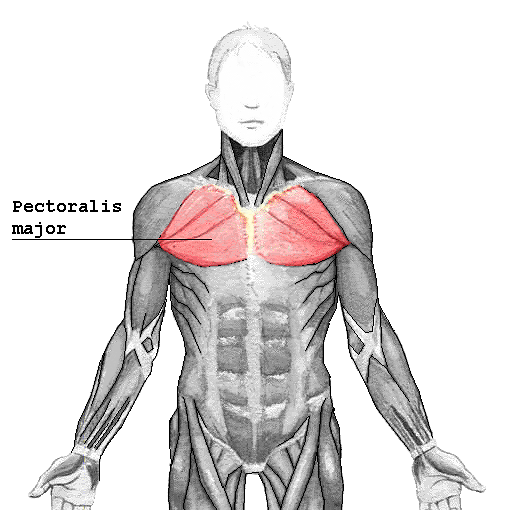 Most superficalmuscle of the upper chest -- Prime moverof arm flexion, Rotates arm medially, Adducts arm against resistance, Lifts rib cage -- clavicle, sternum, ribs 1-6 -- greater tubercle of humerus |
|
Pectoralis minor: location, action, origin, insertion
|
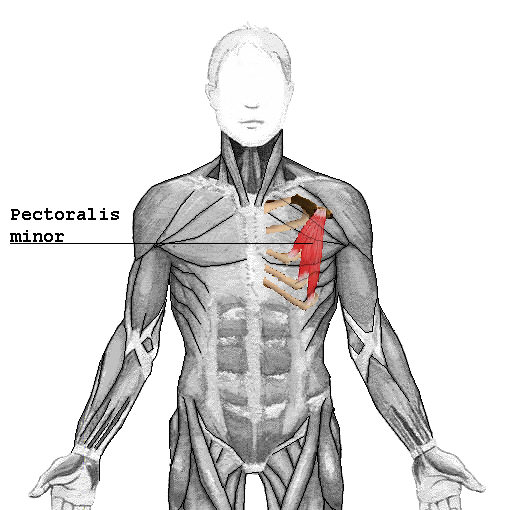 Directly beneath pec major -- moves scapula forward and down, draws ribs superiorly -- ribs 3-5 -- coracoid process |
|
Latissimus dorsi: location, action, origin, insertion
|
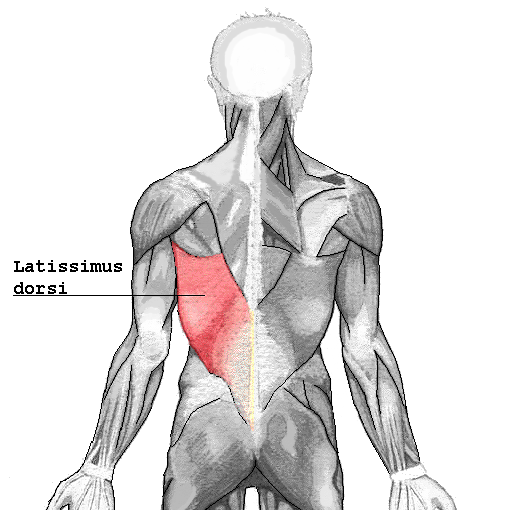 Lower back muscle, Triangle shaped -- Prime moverof arm extension, Arm adductor and medial rotator, Depresses scapula -- spine of last 6 T and all L vertebrae, lower 3-4 ribs and illiaccrest -- intertuberculargroove of humerus |
|
Deltoid: location, action, origin, insertion
|
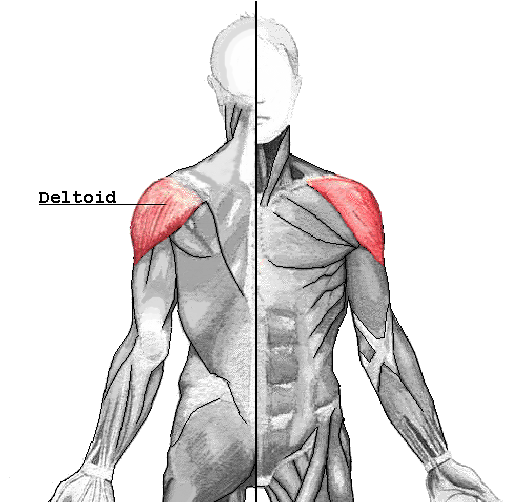 Forms rounded shoulder -- prime mover of arm abduction, antagonist of pec major and latissimus dorsi, can flex, extend, and rotate arm -- Trapezius, lateral clavicle, and scapula -- Deltoid tuberosity |
|
Hi
|
Hi
|
|
Rotator cuff muscles: function and the 4 (SITS)
|
Originate from scapula and their tendons blend with the fibrous capsule of the shoulder joint en route to the humerus, Main function is to reinforce the shoulder capsule to prevent dislocation of the humerus -- Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teresminor, Subscapularis
|
|
Subscapularis: location, function, origin, insertion
|
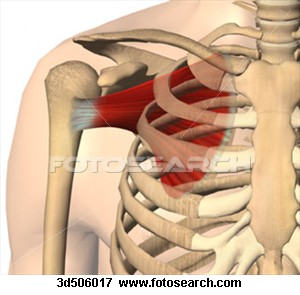 Anterior scapula -- Rotator cuff muscle, Prime medial rotatorof humerus, Stabilizes shoulder joint -- subscapular fossa -- Lesser tubercle of humerus |
|
Supraspinatus: location, function, origin, insertion
|
Deep muscle, superior to spine of scapula -- Stabilizes shoulder joint, Assists with abduction -- supraspinaous fossa -- Superior greater tubercle
|
|
Infraspinatous: location, function, origin, insertion
|
Deep muscle inferior to spine or scapula -- Rotates arm laterally, Holds humerus in joint cavity -- infraspinaous fossa -- Greater tubercle, posterior to supraspinatus
|



