Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
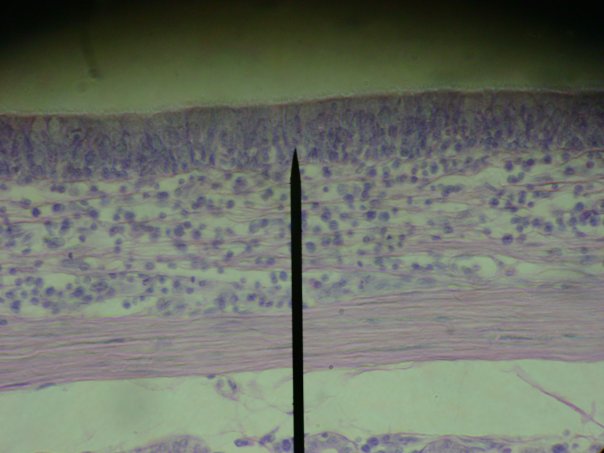 Consists of cells of different heights that rest on same basement membrane, but the nuclei are located at different levels so the tissue appears to have multiple layers. * secretes mucus; moves mucus by ciliary action * lines most of upper respiratory tract * lines portions of male reproductive tract |
Psuedostratified Columnar (Epithelial Tissue)
|
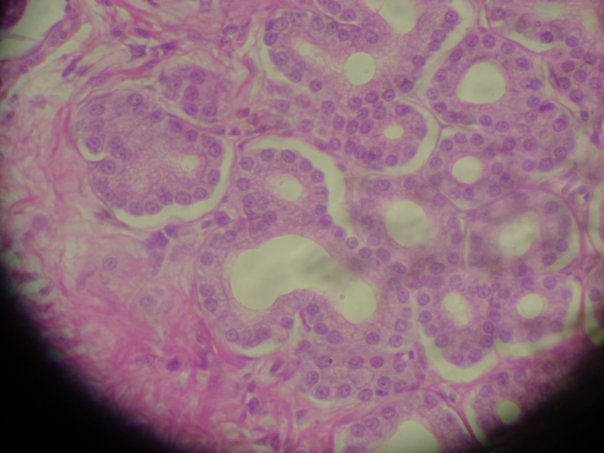 Consists of elongated rectangular cells, each with a single nucleus located near the base of the cell. * secretion; absorption * non-ciliated columnar epithelium in small intestine contains goblet cells that secrete mucus and microvilli that increase surface area to enhance absorption * ciliated columnar epithelium in uterine tubes moves oocytes toward uterus |
Simple Columnar (Epithelial Tissue)
|
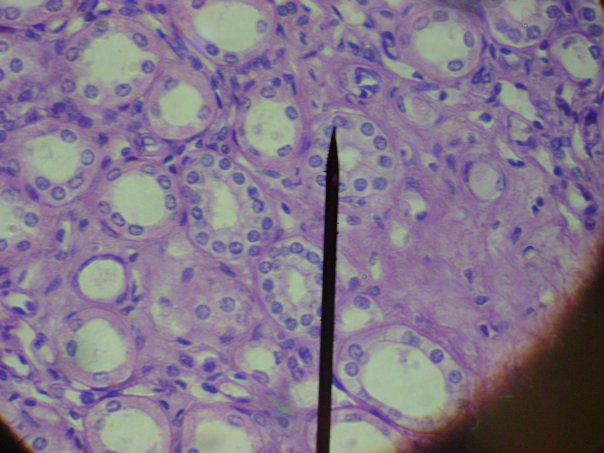 Consists of squarish cells, each with a spherical central nucleus. * absorption; secretion * kidney tubules and lining of ducts of salivary glands |
Simple Cuboidal (Epithelial Tissue)
|
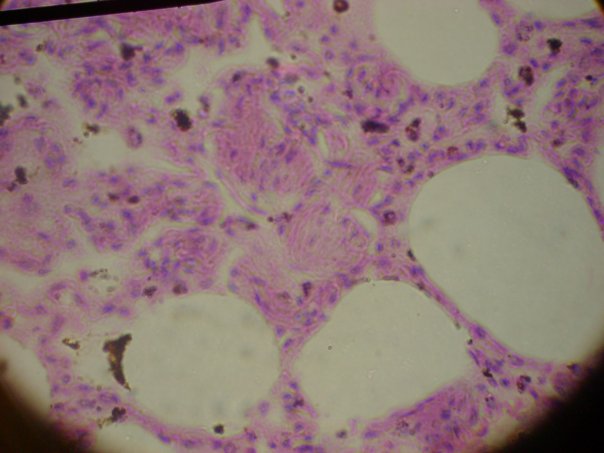 Consists of thin, flat, irregular cells, each with one central nucleus. * diffusion; osmosis; filtration * lungs and kidneys * mesothelium lines abdominal cavity, pleural cavities, pericardial cavities * endothelium lines heart and blood vessels |
Simple Squamos (Epithelial Tissue)
|
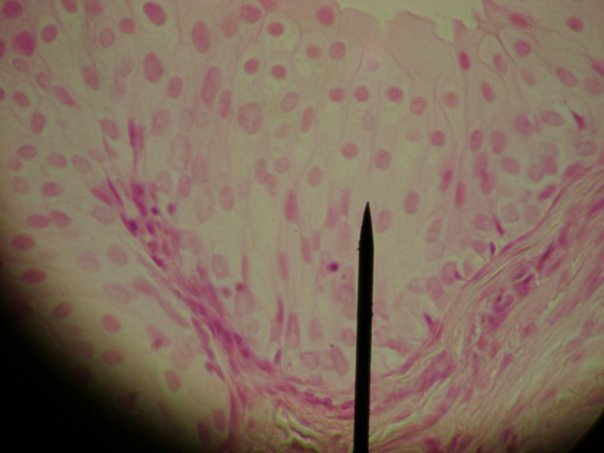 consists of two or more layers of cube shaped cells. * protection; limited secretion; absorption * ducts of sweat glands * ovaries and testes |
Stratified Cuboidal (Epithelial Tissue)
|
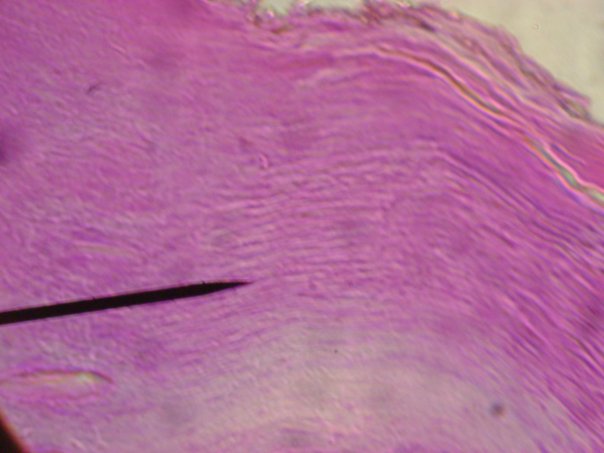 consists of multiple layers of cells. * deep cuboidal or columnar cells become squamous near apical surface * protects against pathogens; resists abrasion; retards water loss * keratinized epithelium on skin surface contains layer of dead squamous cells filled with waterproof keratin protein * non-keratinized epithelium covers tongue, lines mouth, esophagus, anal canal, vagina; because it lacks a surface layer of dead squamous cells it is moist and slippery |
Stratified Squamos (Epithelial Tissue)
|
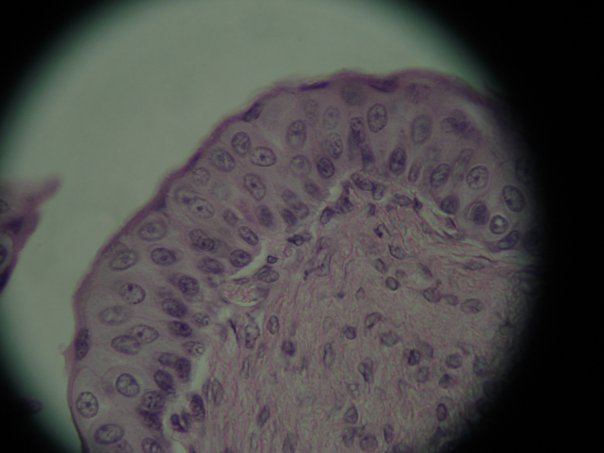 Consists of rounded or cuboidal cells that become squamous cells as the tissue stretches. * permits distension of an organ or structure * located in ureters, urinary bladder, part of urethra |
Transtional (Epithelial Tissue)
|
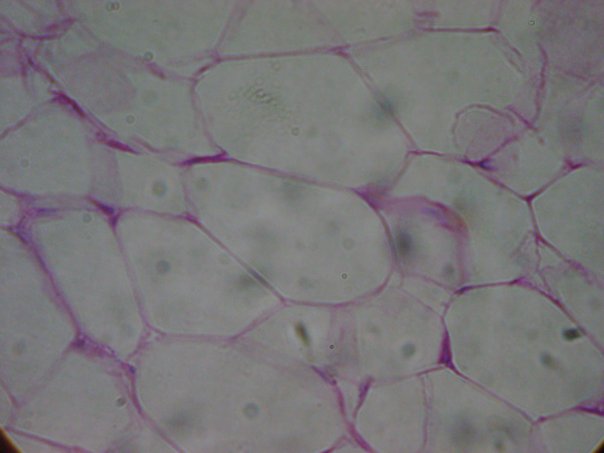 contains relatively few fibers, but many adipocytes that are filled with large fat droplets. * protective cushion, insulates against heat loss, stores energy * located in subcutaneous “fat layers” beneath skin, in breasts, on hips * located around kidneys, heart, and various joints * amount of adipose tissue depends upon amount of food consumed - overeating results in obesity because excess food is converted to fat |
Adipose (Loose Connective Tissue)
|
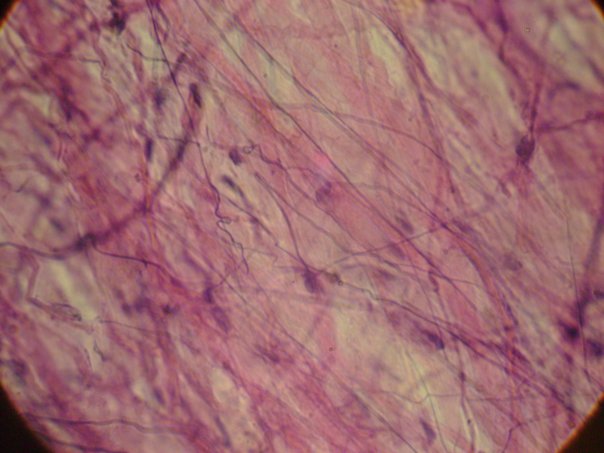 Consists of collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and reticular fibers and cells that are embedded in a semi-fluid ground substance. * binds epithelium to tissue; provides strength and support * thin, delicate membranes located beneath skin * located between skin and muscles * located around blood vessels and nerves |
Areolar (Loose Connective Tissue)
|
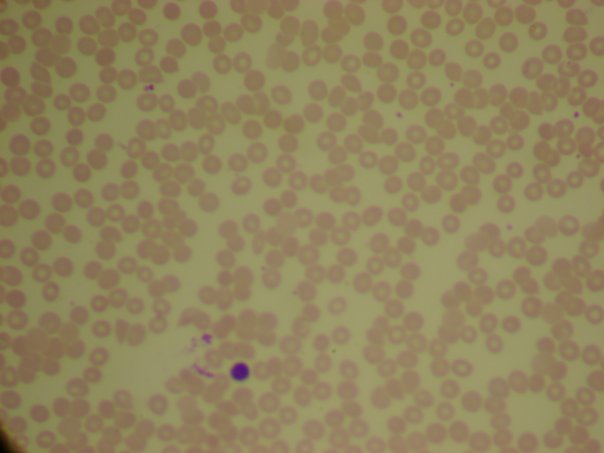 Blood is a fluid connective tissue whose ground substance is called plasma Suspended in the plasma are red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and various fibers. Blood transports cells and dissolved substances throughout the body. |
Blood (Connective Tissue)
|
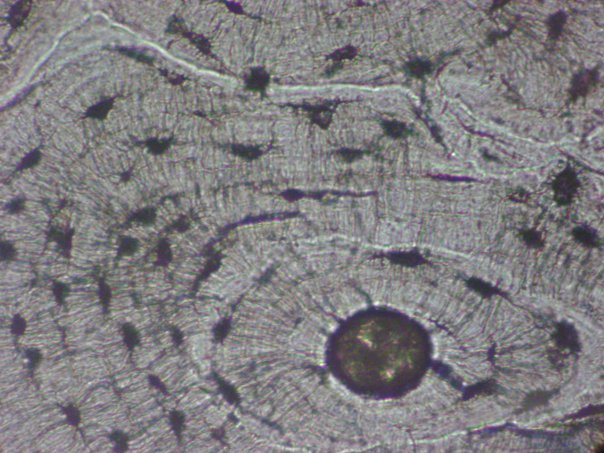 There are two types of osseous tissue. * spongy bone consists of trabeculae (lightweight bony plates) * compact bone consists of dense calcified osteons - hardest type of CT, because of calcium salts and chondroitin sulfate around collagen fibers in matrix provides physical support for the body, protects internal organs, provides leverage for muscle action, and stores minerals (mostly calcium and phosphorus). Mature cells are called osteocytes. |
Bone (Connective Tissue)
|
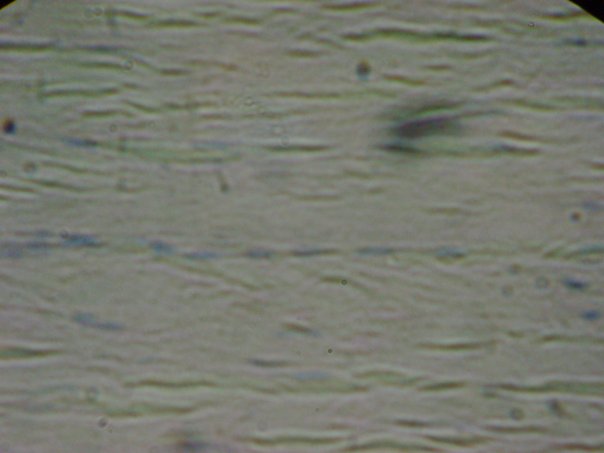 Contains parallel bundles of collagen fibers. * its orderly arrangement provides strength * principal component of tendons and ligaments |
Dense Regular (Connective Tissue)
|
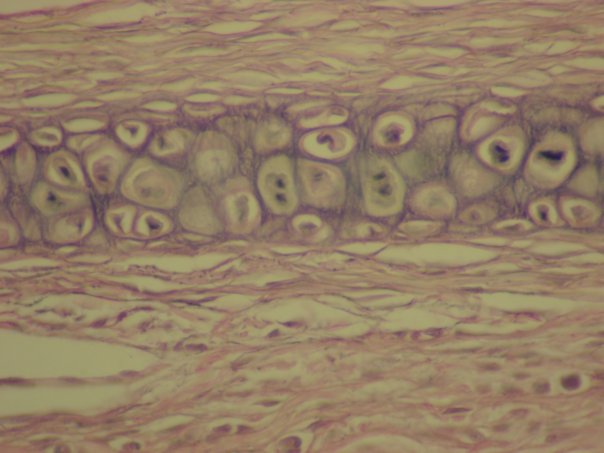 Contains chondrocytes within a web-like mesh of elastic fibers. * provides strength and flexible elastic support * maintains shape of external ear and epiglottis |
Elastic Cartilage (Connective Tissue)
|
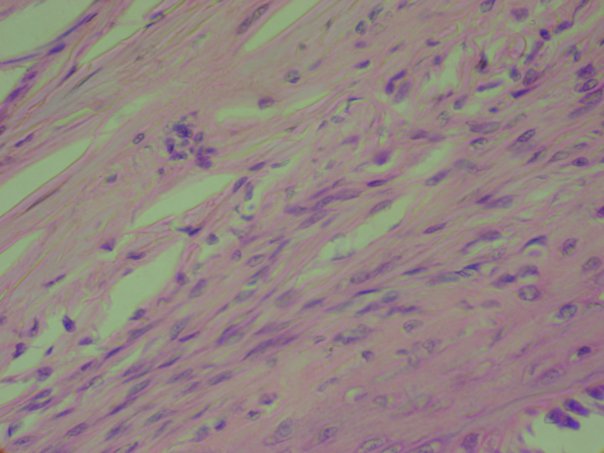 Contains chondrocytes among collagen fibers, but is not enclosed in a perichondrium. * absorbs shock; provides support * located in pubic symphysis and in intervertebral discs * forms shock-absorbing pads in knees |
Fibrocartilage (Connective Tissue)
|
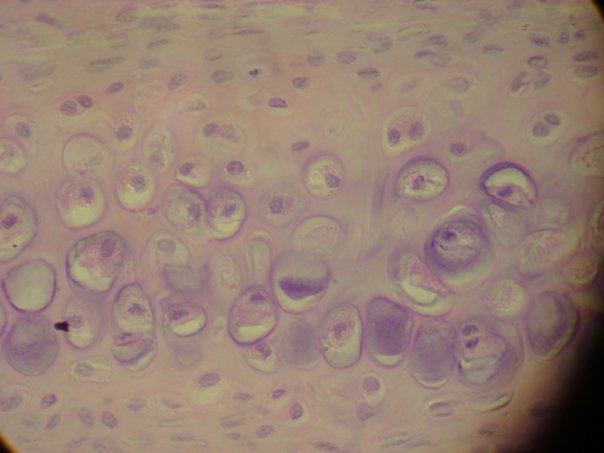 Has a glossy, bluish-white appearance and is the most abundant type of cartilage. * matrix for bone development; provides friction-free movement at joints * articular cartilage located at ends of long bones * costal cartilage located at ends of ribs * located at tip of nose, parts of larynx, trachea, bronchi |
Hyaline Cartilage (Connective Tissue)
|



