Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
What are the 3 patterns of hormone secretion?
|
Constant secretion
acute response
cyclic secretion
|
|
Define constant secretion
|
Hormones are constantly produced by the body, the control mechanisms simply raise or lower this constant level of secretion.
|
|
Define acute response
|
Hormone -very low levels until a particular stimulus occurs. production increases quickly. Once the stimulus goes away,production drops off quickly.
|
|
Define cyclic secretion
|
Hormones which follow this pattern are secreted on a regular, predictable cycle.
|
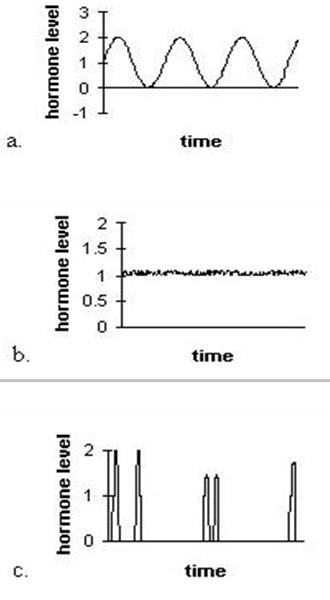 The graphs below illustrate the level of hormones in the body at a given time. Indicate which of the three secretion patterns they represent. |
The graph in (a) represents the cyclic secretion
The graph in (b) is constant secretion
The graph in (c) represents acute response
|
|
What are the two types of hormone receptors?
|
Membrane-bound receptors and intracellular receptors
|
|
Define membrane-bound receptors
|
Membrane-bound receptors are located on the plasma membrane of the target cell. The hormone fits into the receptor like a key fits into a lock.
|
|
Define intracellular receptors
|
A hormone interacts with a receptor, stimulating the cell to synthesize and secrete a new protein.
|
|
A hormone interacts with a receptor, stimulating the cell to synthesize and secrete a new protein. Is the receptor intracellular or membrane-bound?
|
Intracellular receptor
|
|
What kinds of hormones stimulate membrane-bound receptors?
|
Protein or peptide hormones and Some amine hormones.
|
|
What kind of receptor is used to respond to the sex hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone)?
|
Sex hormones are steroids, so they must reach intracellular receptors
|
|
Epinephrine increases certain smooth muscle contractions by stimulating the release of calcium ions in the smooth muscle cell. Is the receptor intracellular or membrane-bound?
|
Membrane-bound receptor
|
|
Define Prostaglandins -
|
Biologically active lipids which produce many effects in the body, including smooth muscle contractions, inflammation, and pain.
|
|
What do prostaglandins do?
|
Biologically active lipids which produce many effects in the body, including smooth muscle contractions, inflammation, and pain
|



