Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
|
Irreversible Stage of Shock
BP?
Renal & Liver functions?
Judgement that shock is irreversible only made ______________?
|
BP remains low.
Renal & Liver functions fail.
...only made "after the fact"
|
|
Which stage of shock is characterized by a normal blood pressure?
|
Compensatory
|
|
General Management strategies in shock
|
Flued replacement - crystalloid, colloid solutions (colloid solution is very expensive)
Nutritional support
Vasoactive medication therapy
Restore intravasular volume
|
|
What is normal stroke volume? (what's left in the heart after contraction/ejection)
|
60 - 80 mL
|
|
Position for hypovolemic shock?
|
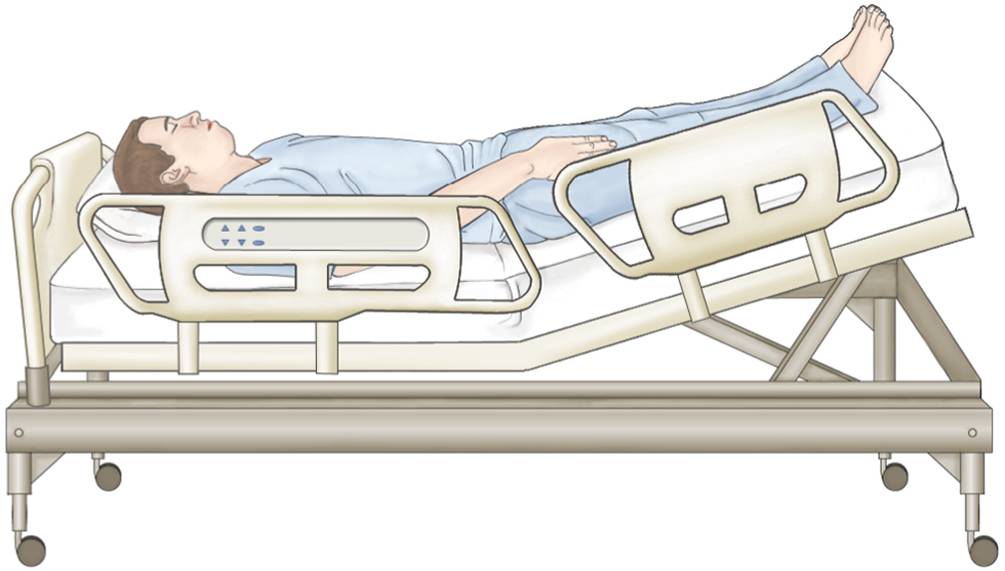 Modified Trendelenburg (feet raised) - assists with fluid redistribution & venous return |
|
Pathophysiology of cardiogenic shock
|
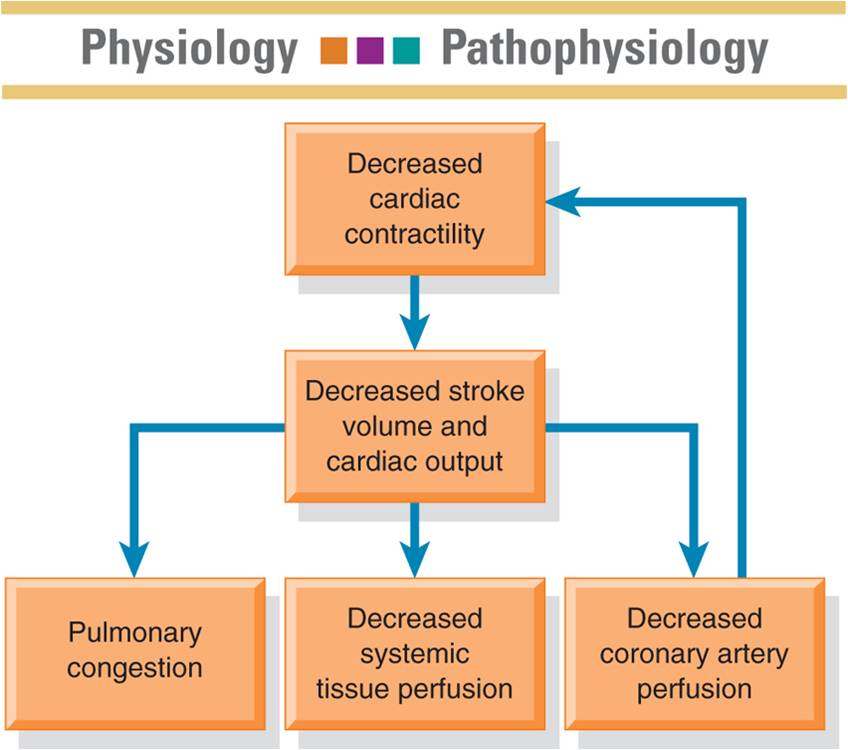 Chest pain, fatigue, impending doom |
|
Labs for cardiogenic shock
|
BNP, tryponin, creatinine
|
|
Cardiogenic shock - what does morphine do?
|
Morphine helps dilate the blood vessles, reducees work of heart. Watch Respiratory rate!!!! Morphine: 2-4mg every 5 min (max)
|
|
Cardiogenic shock - what pharmacologic therapies?
|
Dobutamine
Nitroglycerin
Dopamine
vasoactive medication
antiarrhythmic meds
|
|
Circulatory shock types?
What's common among them?
|
Septic, Neurogenic and Anaphylactic shock
Massive vasodilation, blood pools in peripheral vessels
|
|
Most common of the circulatory shocks
|
Septic shock
|
|
Common characteristic of Neurogenic shock?
|
Bradycardia
|
|
Anaphylactic shock - patient may experience ___________? What is used to treat this?
|
May experience hypotension and severe respiratory distress.
Epi-pen, benadryl, or albuterol inhaler.
|
|
Pathophysiology of Circulatory Shock
|
Precipitating event
Vasodilation
Activation of inflammatory response
Maldistribution of blood volume
Decreased venous return
Decreased cardiac outpout
Decreased tissue perfusion
|
|
3 things to manage all types of shock
|
Fluid replacement
vasoactive meds
Nutritional support (to address metabolic requirements)
|



