Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Nam this substituent |
Isopropyl
|
 Name this substituent |
Neopentyl
|
 Name this substituent |
T-butyl
|
 Name this substituent |
Sec-butyl
|
 Name this substituent |
Isobutyl
|
 Which organic molecules have this formula? |
Alkanes
|
|
NOMENCLATURE (Alkanes)1. Find the longest chain.2. Number the chain.3. Name subtituents4. Prefixes such as di, tri, tert, sec..etc are ignored in alphabetizing; cyclo, iso and neo are included in alphabetization.
|
Review
|
 Which organic molecules have this formula? |
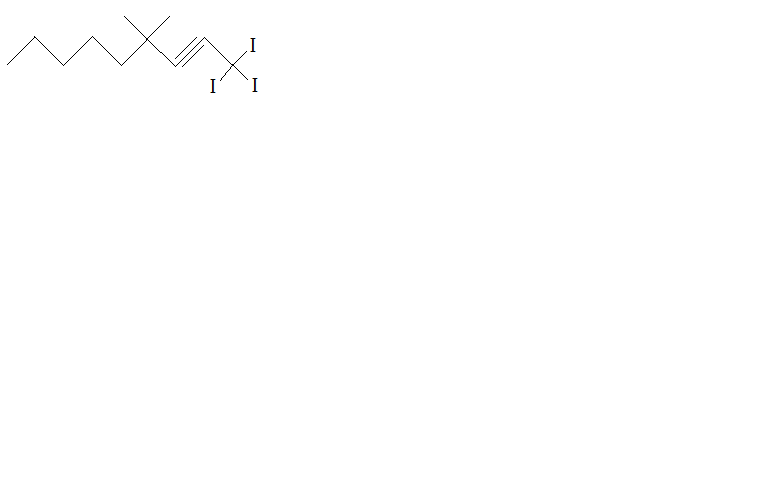 Alkenes |
|
Nomenclature (Alkenes)
In naming alkenes, the double bond receives the lowest possible number; note any isomers cis/trans and Z/E. Multiple double bonds must be names using prefixes di-, tri-, etc. |
Review
|
|
Nomenclature (Alkenes)CH2 groups are referred to as methylene |
Methylene cyclohexane
|
 Nomenclature (Alkenes)Monosubstituted ethylenes (2 carbons) are referred to as vinyl groups. |
Review
|
 Nomenclature (Alkenes)Allyl groups are propylene's substituted at the C-3 position. |
Allyl chloride
|
 Which organic molecules have this formula? |
Alkyne
|
|
NomenclatureSubstituted Alkanes: Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes are compounds that contain a halogen substituent. These compounds may be named as alkyl halides. ex: ethyl (2 carbons) chloride Substituted Alkanes: AlcoholsAlcohols are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding alkane with -ol. Priority is given to the carbon with the -OH group. Molecules with two hydroxyl groups are termed diols or ____ and have the suffix -diol. When two hydroxyl groups are on adjacent carbons the groups are called _____; when they are on the same carbon they are called ____. Geminal diols are called _____ and are less common than vicinal diols due to their tendency to spontaneously lose water to produce a C=O compound. |
Glycols; vicinal; geminal
hydrates |
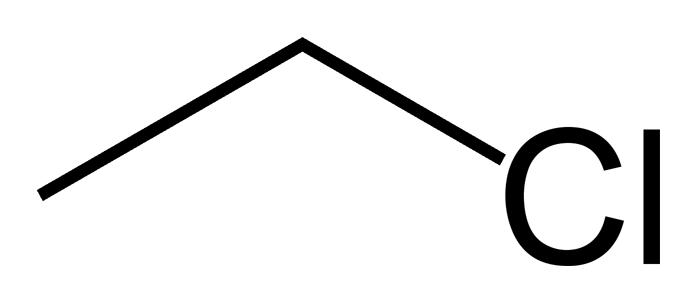 What type of compound is this? |
Alkyl halide
|



