Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
 Map key/ legend Pg. #14 |
Identifies the symbols on a map and what they represent
|
 Map symbolsPg. #14 |
A symbol that represents something on a map
|
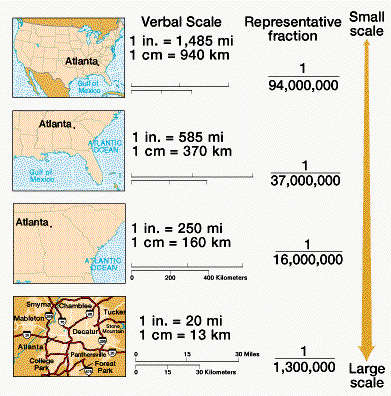 Distance scalePg. #14 |
Helps determine real distances between points on a map
|
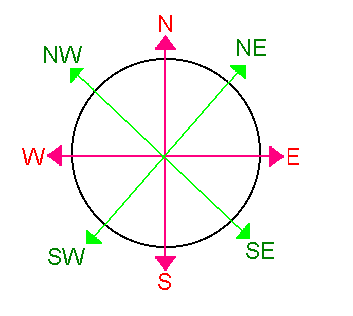 Compass rosePg. #14 |
A directional indicators that has arrows that point to all four principal directions
|
 Cardinal directionsPg. #14 |
The four main directions (North, South, East, and West)
|
 Intermediate directionsPg. # |
The directions halfway between the cardinal directions (northwest, northeast, southeast, southwest)
|
 Map projectionsPg. #11 |
Different ways mapmakers present our round Earth on flat maps (have some distortion)
|
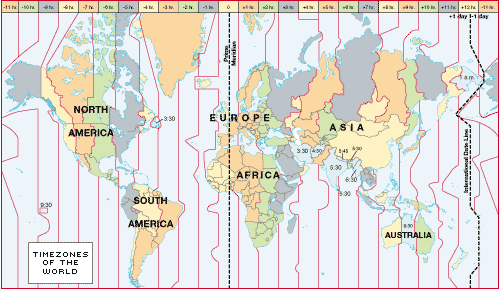 Time zonePg. #32-33 |
The world is divided into 24 15 degrees in longitude width time zones
|
 LatitudePg. #9 |
Lines on a globe drawn in an east-west direction and measured in degrees
|
 LongitudePg. #9 |
Lines on a globe drawn in a north-south direction and measured in degrees
|
 HemispherePg. #10 |
Halves of the globe divided by the equator and prime meridian
|
 PolesPg. #S41 |
The most northern or southern point on Earth
|
 Physical mapPg. #16 |
Shows natural features like mountains, rivers, and other bodies of water
|
 Political mapPg. #16 |
Shows the world's borders, cities, countries, states, and other political features
|
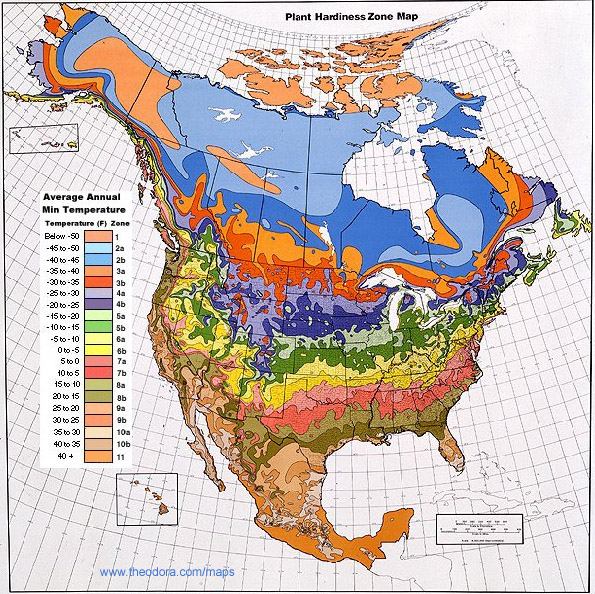 Special purpose mapPg. #15,16 |
Focuses on a specific place or region with certain kinds of information such as climate, precipitation, population, and economic features
|



