Cards In This Set
| Front | Back |
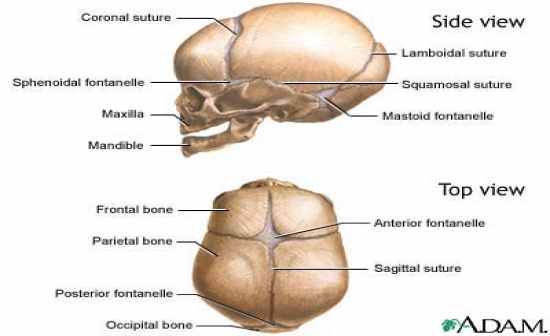 Bony Joints |
Synostosis
synarthrotic ossification of fibrous or cartilaginous joints |
|
Fibrous Joints
|
Synarthrotic
or synarthrodial joint adjacent bones are bound by collagen fibers that emerge from one bone sutures, gomphoses, and syndesmoses |
|
sutures
|
Synarthrotic
|
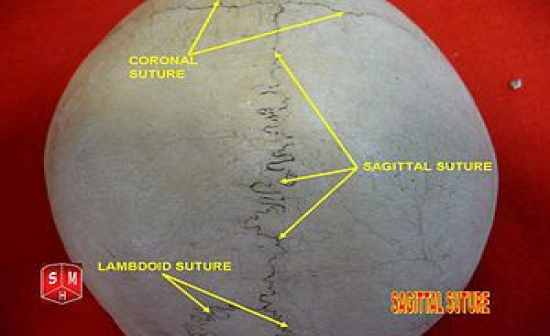 sagittal suture |
Between parietal bones
|
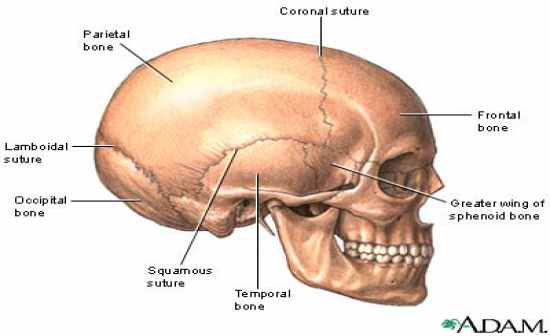 coronal suture |
At the anterior margin
|
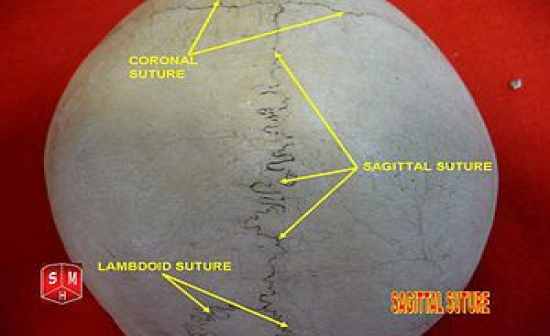 lambdoid suture |
At the posterior margin
|
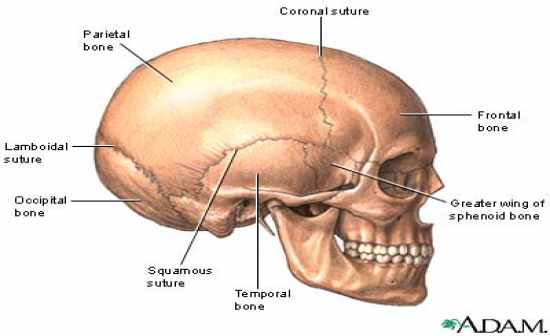 squamous suture |
Laterally
|
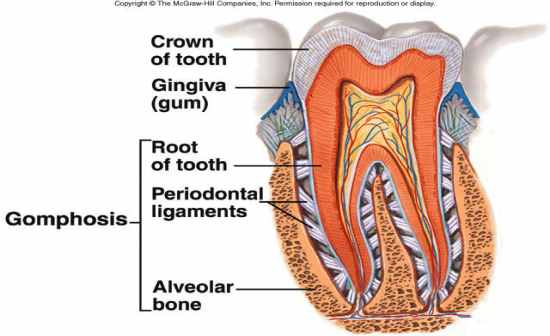 gomphoses |
Synarthrotic
|
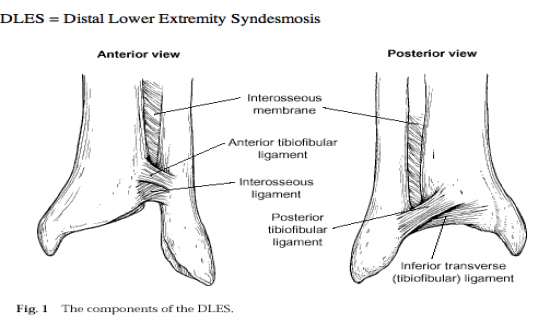 syndesmoses |
Amphiarthrotic
|
|
Cartilaginous joints
|
Amphiarthrosis
two bones linked by cartilage |
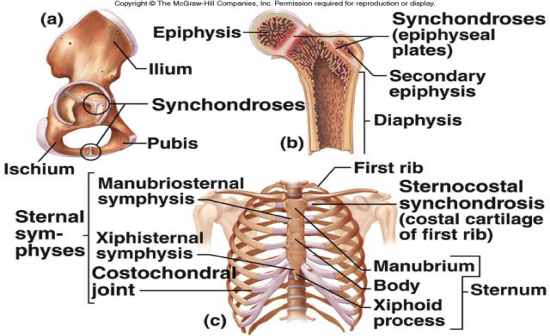 Synchrondroses |
Synarthrotic
bones are bound by hyaline cartilage between epiphysis and diaphysis of a long bone first rib to the sternum by a hyaline costal cartilage |
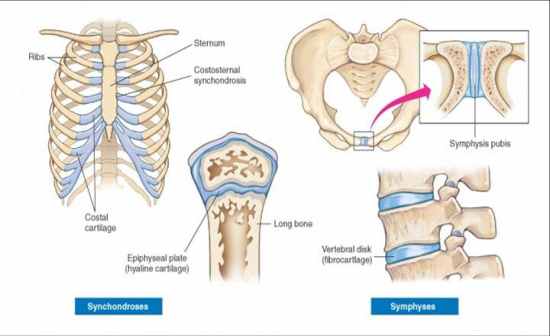 symphyses |
Amphiarthrotic
two bones joined by fibrocartilage pubic symphysis- R and L pubic bones are joined by the cartilaginous interpubic disc |
|
synovial joints
|
Diarthrotic
|
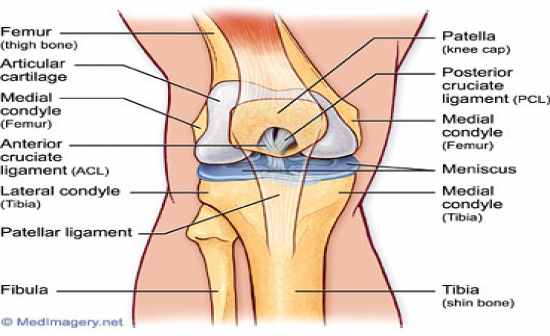 articular cartilage |
In synovial joints
facing smooth surfaces of the two bones are covered in this hyaline cartilage |
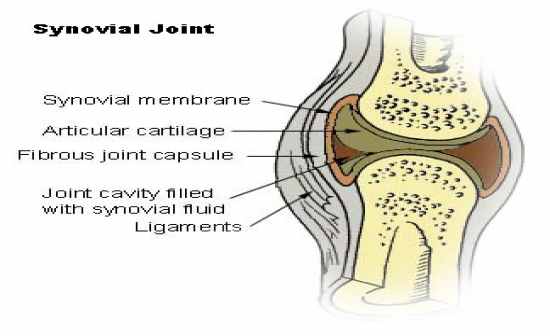 joint (articular cavity) synovial fluid joint (articular) capsule fibrous capsule synovial membrane |
--
|



